Analysis of H3K27me3 expression and DNA methylation at CCGG sites in smoking and non-smoking patients with non-small cell lung cancer and their clinical significance
- PMID: 29616099
- PMCID: PMC5876441
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.8100
Analysis of H3K27me3 expression and DNA methylation at CCGG sites in smoking and non-smoking patients with non-small cell lung cancer and their clinical significance
Abstract
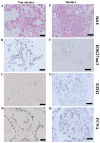
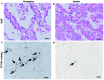
Smoking frequently leads to epigenetic alterations, including DNA methylation and histone modifications. The effect that smoking has on the DNA methylation levels at CCGG sites, the expression of trimethylation of histone H3 at lysine 27 (H3K27me3) and enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2), and their interactions in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) were analyzed. There were a total of 42 patients with NSCLC, 22 with adenocarcinomas and 20 with squamous cell carcinomas enrolled in the present study. Expression of H3K27me3, EZH2 and proliferating cellular nuclear antigen (PCNA) were immunohistochemically detected. DNA methylation at CCGG sites was evaluated via histoendonuclease-linked detection of DNA methylation sites. The apoptotic index of cancerous tissues obtained from patients of different smoking statuses was evaluated via the terminal deoxynucleotidyl-transferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling method. The association with clinicopathological data was calculated relative to different smoking statuses. Compared with the non-smokers, smokers with NSCLC exhibited a significantly lower apoptotic index (P<0.05), and frequently had a lower level of DNA methylation at CCGG sites, lower H3K27me3 expression and a higher EZH2 expression (P<0.05). DNA methylation levels at CCGG sites were negatively correlated to the Brinkman index (P=0.017). Furthermore, there was a parallel association between the H3K27me3 and EZH2 expression levels in the majority of smokers, whereas in the majority of non-smokers, there was a diverging association (P=0.015). There was a diverging association between the PCNA and EZH2 expression levels in the majority of smokers; however, in the majority of non-smokers, there was a parallel association (P=0.048). In addition, the association between the CCGG methylation ratio and immunohistochemical expression of H3K27me3 was a parallel association in the majority of smokers, while in the majority of non-smokers there was a diverging association (P=0.049). Conclusively, patients with NSCLC and different smoking statuses exhibit different epigenetic characteristics. Additionally, DNA methylation levels at the CCGG sites may have the ability to determine associations between the expression levels of H3K27me3, EZH2 and PCNA.
Keywords: DNA methylation; EZH2; non-small cell lung cancer; smoking; trimethylation of histone H3 at lysine 27.
Figures



Similar articles
-
High expression of trimethylated histone H3 at lysine 27 predicts better prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer.Int J Oncol. 2013 Nov;43(5):1467-80. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.2062. Epub 2013 Aug 20. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23969945
-
Yin Yang 1-mediated epigenetic silencing of tumour-suppressive microRNAs activates nuclear factor-κB in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Pathol. 2016 Apr;238(5):651-64. doi: 10.1002/path.4688. J Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26800240
-
The association between histone 3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) and prostate cancer: relationship with clinicopathological parameters.BMC Cancer. 2014 Dec 23;14:994. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-994. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25535400 Free PMC article.
-
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with histone H3 trimethylation at lysine 27: another poor prognostic phenotype independent of c-Myc/Bcl2 coexpression.Hum Pathol. 2014 Oct;45(10):2043-50. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2014.07.002. Epub 2014 Jul 23. Hum Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25149548
-
Epigenetic regulation of cancer progression by EZH2: from biological insights to therapeutic potential.Biomark Res. 2018 Mar 9;6:10. doi: 10.1186/s40364-018-0122-2. eCollection 2018. Biomark Res. 2018. PMID: 29556394 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multiplexed protein profiling reveals spatial subcellular signaling networks.iScience. 2022 Aug 18;25(9):104980. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104980. eCollection 2022 Sep 16. iScience. 2022. PMID: 36093051 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of long noncoding RNA PVT1 inhibits podocyte damage and apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy by upregulating FOXA1.Exp Mol Med. 2019 Aug 1;51(8):1-15. doi: 10.1038/s12276-019-0259-6. Exp Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31371698 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenome-Wide Tobacco-Related Methylation Signature Identification and Their Multilevel Regulatory Network Inference for Lung Adenocarcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Apr 24;2020:2471915. doi: 10.1155/2020/2471915. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32420331 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid biopsies based on DNA methylation as biomarkers for the detection and prognosis of lung cancer.Clin Epigenetics. 2022 Sep 24;14(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s13148-022-01337-0. Clin Epigenetics. 2022. PMID: 36153611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RUNX3/H3K27me3 Co-Expression Defines a Better Prognosis in Surgically Resected Stage I and Postoperative Chemotherapy-Naive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.J Oncol. 2022 Mar 24;2022:5752263. doi: 10.1155/2022/5752263. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35368900 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Piyathilake CJ, Frost AR, Bell WC, Oelschlager D, Weiss H, Johanning GL, Niveleau A, Heimburger DC, Grizzle WE. Altered global methylation of DNA: An epigenetic difference in susceptibility for lung cancer is associated with its progression. Hum Pathol. 2001;32:856–862. doi: 10.1053/hupa.2001.26471. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
