Diagnosis and treatment of submucous myoma of the uterus with interventional ultrasound
- PMID: 29616100
- PMCID: PMC5876458
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2018.8122
Diagnosis and treatment of submucous myoma of the uterus with interventional ultrasound
Abstract
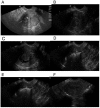
The value of interventional ultrasound in the diagnosis and treatment of submucous myoma of the uterus was assessed to study the ultrasonographic features of modified sonohysterography for submucous polyp of uterus. A total of 25 patients diagnosed preliminarily as submucous myoma of the uterus via conventional ultrasound examination from June 2014 to December 2016 were enrolled in the study. The diagnosis was made via the comprehensive analysis of ultrasound-guided modified SHG, followed by ultrasound-guided needle biopsy and sclerotherapy of tumor. After modified SHG and ultrasound-guided needle biopsy, 96% (24/25) cases were confirmed pathologically as submucous myoma of the uterus. After treatment, the maximum diameter of myoma in patients with submucous myoma of uterus was significantly different, and the volume of myoma was significantly reduced. After treatment, the clinical symptoms of patients with submucous myoma of the uterus were obviously improved compared to before treatment (P<0.05). It was found in the follow-up after treatment that a small number of patients suffered from mild abdominal pain, increased secretion, slight vaginal bleeding, cold sweat, pale complexion, dizziness and other symptoms, which, however, disappeared after treatment for about 1 week. The score of 36 item Short-Form Health Survey Questionnaire of patients with submucous myoma of the uterus was significantly different before and after treatment (P<0.05). Interventional ultrasonography can effectively diagnose the submucous myoma of uterus. The treatment of submucous myoma of uterus with ultrasound-guided intratumor injection of lauromacrogol is characterized by simple operation, which can effectively reduce the tumor diameter and volume, improve the blood flow in patients, reduce the postoperative adverse reactions and alleviate the patient's pain, so it is a new type of minimally invasive treatment method of submucous myoma of the uterus, and it is worthy of clinical promotion and application.
Keywords: interventional ultrasound; lauromacrogol; submucous myoma of the uterus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Non-puerperal uterine inversion due to submucous myoma in a young woman: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2010 Jan 24;4:21. doi: 10.1186/1752-1947-4-21. J Med Case Rep. 2010. PMID: 20205761 Free PMC article.
-
Modified hysteroscopic myomectomy of large submucous fibroids.Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2003;56(4):192-6. doi: 10.1159/000074451. Epub 2003 Oct 23. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2003. PMID: 14576470
-
Use of strict sonohysterographic methods for preoperative assessment of submucous myomas.Fertil Steril. 2003 Apr;79(4):998-1002. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(02)04916-6. Fertil Steril. 2003. PMID: 12749444 Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment of uterine fibroids for abnormal uterine bleeding: myomectomy and uterine artery embolization.Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2007 Dec;21(6):995-1005. doi: 10.1016/j.bpobgyn.2007.03.017. Epub 2007 May 2. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2007. PMID: 17478123 Review.
-
[New options in the diagnosis and management of uterine myoma].Med Arh. 2008;62(4):234-9. Med Arh. 2008. PMID: 19145810 Review. Bosnian.
Cited by
-
A Case Report of the Largest Submucosal Uterine Leiomyoma Removed by Single-Session Hysteroscopic Myomectomy in the Caribbean.Cureus. 2022 Mar 9;14(3):e22985. doi: 10.7759/cureus.22985. eCollection 2022 Mar. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35464500 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review of Minimally Invasive Approaches to Uterine Fibroid Treatment for Improving Quality of Life and Fibroid-Associated Symptoms.Reprod Sci. 2023 May;30(5):1495-1505. doi: 10.1007/s43032-022-01120-9. Epub 2022 Nov 18. Reprod Sci. 2023. PMID: 36401073
-
A 63-Year-Old Postmenopausal Woman with Uterine Inversion Associated with a Submucosal Geburt Fibroid Successfully Treated by Surgical Reversal Using the Spinelli Procedure.Am J Case Rep. 2023 Jan 16;24:e938390. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.938390. Am J Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 36642936 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beckmann MW, Juhasz-Böss I, Denschlag D, Gaß P, Dimpfl T, Harter P, Mallmann P, Renner SP, Rimbach S, Runnebaum I, et al. Surgical methods for the treatment of uterine fibroids - risk of uterine sarcoma and problems of morcellation: Position paper of the DGGG. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2015;75:148–164. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1545684. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ananthakrishnan G, Murray L, Ritchie M, Murray G, Bryden F, Lassman S, Lumsden MA, Moss JG. Randomized comparison of uterine artery embolization (UAE) with surgical treatment in patients with symptomatic uterine fibroids (REST trial): Subanalysis of 5-year MRI findings. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2013;36:676–681. doi: 10.1007/s00270-012-0485-y. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Negm SM, Kamel RA, Momtaz M, Magdi AM, Azab HS. Correlation between three dimensional multi-slice sonohysterography and hysteroscopy in the diagnosis and classification of submucous myomas. Middle East Fertil Soc J. 2010;15:209–215. doi: 10.1016/j.mefs.2010.07.004. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
