Specific Chemical and Genetic Markers Revealed a Thousands-Year Presence of Toxic Nodularia spumigena in the Baltic Sea
- PMID: 29617355
- PMCID: PMC5923403
- DOI: 10.3390/md16040116
Specific Chemical and Genetic Markers Revealed a Thousands-Year Presence of Toxic Nodularia spumigena in the Baltic Sea
Abstract
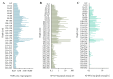
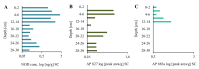
In the Baltic Sea, diazotrophic cyanobacteria have been present for thousands of years, over the whole brackish water phase of the ecosystem. However, our knowledge about the species composition of the cyanobacterial community is limited to the last several decades. In the current study, the presence of species-specific chemical and genetic markers in deep sediments were analyzed to increase the existing knowledge on the history of toxic Nodularia spumigena blooms in the Baltic Sea. As chemical markers, three cyclic nonribosomal peptides were applied: the hepatotoxic nodularin, which in the sea was detected solely in N. spumigena, and two anabaenopeptins (AP827 and AP883a) characteristic of two different chemotypes of this species. From the same sediment samples, DNA was isolated and the gene involved in biosynthesis of nodularin, as well as the phycocyanin intergenic spacer region (PC-IGS), were amplified. The results of chemical and genetic analyses proved for the first time the thousands-year presence of toxic N. spumigena in the Baltic Sea. They also indicated that through all this time, the same two sub-populations of the species co-existed.
Keywords: Baltic Sea; anabaenopeptins; cyanobacteria; molecular markers; nodularin; toxin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chemical and Genetic Diversity of Nodularia spumigena from the Baltic Sea.Mar Drugs. 2016 Nov 10;14(11):209. doi: 10.3390/md14110209. Mar Drugs. 2016. PMID: 27834904 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity of toxic and nontoxic nodularia isolates (cyanobacteria) and filaments from the Baltic Sea.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001 Oct;67(10):4638-47. doi: 10.1128/AEM.67.10.4638-4647.2001. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11571167 Free PMC article.
-
Sedimentation of Nodularia spumigena and distribution of nodularin in the food web during transport of a cyanobacterial bloom from the Baltic Sea to the Kattegat.Harmful Algae. 2019 Jun;86:74-83. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2019.05.005. Epub 2019 May 30. Harmful Algae. 2019. PMID: 31358279
-
Bacterial diversity and function in the Baltic Sea with an emphasis on cyanobacteria.Ambio. 2007 Apr;36(2-3):180-5. doi: 10.1579/0044-7447(2007)36[180:bdafit]2.0.co;2. Ambio. 2007. PMID: 17520932 Review.
-
Climate change and regulation of hepatotoxin production in Cyanobacteria.FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2014 Apr;88(1):1-25. doi: 10.1111/1574-6941.12291. Epub 2014 Mar 3. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2014. PMID: 24490596 Review.
Cited by
-
The Diversity of Cyanobacterial Toxins on Structural Characterization, Distribution and Identification: A Systematic Review.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Sep 12;11(9):530. doi: 10.3390/toxins11090530. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31547379 Free PMC article.
-
Cyanobacterial Akinete Distribution, Viability, and Cyanotoxin Records in Sediment Archives From the Northern Baltic Sea.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jun 15;12:681881. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.681881. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34211448 Free PMC article.
-
Interspecific Interactions Drive Nonribosomal Peptide Production in Nodularia spumigena.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Aug 9;88(15):e0096622. doi: 10.1128/aem.00966-22. Epub 2022 Jul 12. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35862669 Free PMC article.
-
Biodiversity of microorganisms in the Baltic Sea: the power of novel methods in the identification of marine microbes.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2024 Sep 18;48(5):fuae024. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuae024. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 39366767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blooms of Toxic Cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena in Norwegian Fjords During Holocene Warm Periods.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Apr 15;12(4):257. doi: 10.3390/toxins12040257. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32326551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bianchi T.S., Westman P., Andrén T., Rolff C., Elmgren R. Cyanobacterial blooms in the Baltic Sea: Natural or human-induced? Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000;45:716–726. doi: 10.4319/lo.2000.45.3.0716. - DOI
-
- Voss M., Kowalewska G., Brenner W. Microfossil and biogeochemical indicators of environmental changes in the Gotland Deep during the last 10.000 years. Baltica. 2001;14:131–140.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

