A practical tool for maximal information coefficient analysis
- PMID: 29617783
- PMCID: PMC5893960
- DOI: 10.1093/gigascience/giy032
A practical tool for maximal information coefficient analysis
Abstract
Background: The ability of finding complex associations in large omics datasets, assessing their significance, and prioritizing them according to their strength can be of great help in the data exploration phase. Mutual information-based measures of association are particularly promising, in particular after the recent introduction of the TICe and MICe estimators, which combine computational efficiency with superior bias/variance properties. An open-source software implementation of these two measures providing a complete procedure to test their significance would be extremely useful.
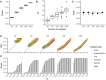
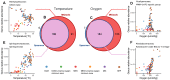
Findings: Here, we present MICtools, a comprehensive and effective pipeline that combines TICe and MICe into a multistep procedure that allows the identification of relationships of various degrees of complexity. MICtools calculates their strength assessing statistical significance using a permutation-based strategy. The performances of the proposed approach are assessed by an extensive investigation in synthetic datasets and an example of a potential application on a metagenomic dataset is also illustrated.
Conclusions: We show that MICtools, combining TICe and MICe, is able to highlight associations that would not be captured by conventional strategies.
Figures



References
-
- Reshef YA, Reshef DN, Finucane HK et al. . Measuring dependence powerfully and equitably. J Mach Learn Res. 2016;17(212):1–63.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

