Comprehensive immunoproteogenomic analyses of malignant pleural mesothelioma
- PMID: 29618661
- PMCID: PMC5928857
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.98575
Comprehensive immunoproteogenomic analyses of malignant pleural mesothelioma
Abstract
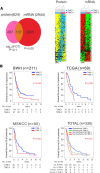
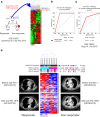
We generated a comprehensive atlas of the immunologic cellular networks within human malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) using mass cytometry. Data-driven analyses of these high-resolution single-cell data identified 2 distinct immunologic subtypes of MPM with vastly different cellular composition, activation states, and immunologic function; mass spectrometry demonstrated differential abundance of MHC-I and -II neopeptides directly identified between these subtypes. The clinical relevance of this immunologic subtyping was investigated with a discriminatory molecular signature derived through comparison of the proteomes and transcriptomes of these 2 immunologic MPM subtypes. This molecular signature, representative of a favorable intratumoral cell network, was independently associated with improved survival in MPM and predicted response to immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with MPM and melanoma. These data additionally suggest a potentially novel mechanism of response to checkpoint blockade: requirement for high measured abundance of neopeptides in the presence of high expression of MHC proteins specific for these neopeptides.
Keywords: Cancer immunotherapy; Expression profiling; Immunology; Oncology; Proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Sugarbaker DJ, Richards WG, Bueno R. Extrapleural pneumonectomy in the treatment of epithelioid malignant pleural mesothelioma: novel prognostic implications of combined N1 and N2 nodal involvement based on experience in 529 patients. Ann Surg. 2014;260(4):577–582. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000000903. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Quispel-Janssen J, et al. A phase II study of nivolumab in malignant pleural mesothelioma (NivoMes): with translational research (TR) biopsies. J Thorac Oncol. 2017;12:S292–S293.
-
- Kindler H, et al. Phase II trial of pembrolizumab in patients with malignant mesothelioma (MM): interim analysis. J Thorac Oncol. 2017;12:S293–S294.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

