Anti-TNF and thiopurine therapy in pregnant IBD patients does not significantly alter a panel of B-cell and T-cell subsets in 1-year-old infants
- PMID: 29618720
- PMCID: PMC5886978
- DOI: 10.1038/s41424-018-0018-3
Anti-TNF and thiopurine therapy in pregnant IBD patients does not significantly alter a panel of B-cell and T-cell subsets in 1-year-old infants
Erratum in
-
Correction: Anti-TNF and thiopurine therapy in pregnant IBD patients does not significantly alter a panel of B-cell and T-cell subsets in 1-year-old infants.Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2018 Jul 31;9(7):172. doi: 10.1038/s41424-018-0040-5. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30065242 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objectives: Infants exposed to combination therapy with anti-tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) agents and thiopurines may exhibit increased infections at 1 year of age compared to unexposed infants. We hypothesized that this increased risk of infection is due to abnormal development of the newborn immune system.
Methods: We immunophenotyped B-cell and T-cell subsets using multiparameter flow cytometry in 1-year-old infants whose mothers were exposed to therapeutic agents for IBD. We analyzed samples from infants exposed to infliximab (IFX) or adalimumab (ADA) monotherapy (IFX/ADA, n = 11), certolizumab pegol (CZP) monotherapy (CZP, n = 4), IFX or ADA plus thiopurine combination therapy (IFX/ADA + IM, n = 4), and CZP plus thiopurine combination therapy (CZP + IM, n = 2).
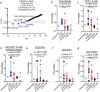
Results: Percentages of B cells, CD4+ T helper cells, T regulatory cells (Tregs), and CD8+ cytotoxic T cells, were similar among the groups. Infants exposed to combination therapy (IFX/ADA + IM) exhibited trends toward fewer CD27+ B cells, switched memory B cells, plasmablasts, interferon gamma (IFNγ)-producing CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and CCR5+CD4+ T cells, but these did not reach statistical significance.
Conclusions: Multiparameter immunophenotyping of major B-cell and T-cell subsets suggests that the adaptive newborn immune system develops largely unaltered after exposure to combination therapy as compared to anti-TNF monotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Bröms G, et al. Birth outcomes in women with inflammatory bowel disease: effects of disease activity and drug exposure. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2014;20:1091–1098. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

