The Hyperglycemic Effect of Melatonin in the Chinese Mitten Crab, Eriocheir sinensis
- PMID: 29618988
- PMCID: PMC5871893
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00270
The Hyperglycemic Effect of Melatonin in the Chinese Mitten Crab, Eriocheir sinensis
Abstract
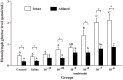
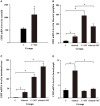
Melatonin has been identified in a variety of invertebrate species, but its function is not as well understood as in crustaceans. The effects of melatonin on hemolymph glucose levels and tissue carbohydrate metabolism in the Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis, were fully investigated in this study. Moreover, whether the eyestalk (an important endocrine center in invertebrate species) involves in this process or not, also were clarified. Analysis revealed that eyestalk ablation, especially bilateral, caused a significant decrease in the hemolymph glucose level. Moreover, injection of melatonin induced hyperglycemia in a dose-dependent manner both in intact and ablated crabs. Based on the expression of CHH mRNA in the 10 different tissues, eyestalk, thoracic ganglion, intestinal tract and hemolymph were selected to estimate the effect of melatonin on the expression of CHH mRNA. Bilateral eyestalk ablation caused a significant increase in the expression of CHH mRNA in the thoracic ganglion, intestinal tract and hemolymph compared with the controls. In addition, injection of melatonin into intact or ablated crabs elevated the CHH mRNA level in the eyestalk, thoracic ganglion and intestinal tract tissues compared with controls. The hemolymph CHH mRNA after melatonin injection was elevated only in ablated crabs. Administration of melatonin resulted in a significant decrease in total carbohydrates and glycogen levels with an increase in phosphorylase activity levels in the hepatopancreas and muscle in intact and ablated crabs. Our findings demonstrated that melatonin can induce hyperglycemic effects in both intact and ablated crabs, suggesting that this effect is probably not mediated solely via eyestalk.
Keywords: Eriocheir sinensis; crustacean hyperglycemic hormone; eyestalk; glucose; melatonin.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Melatonergic regulation of hemolymph sugar levels in the freshwater edible crab, Oziotelphusa senex senex.J Exp Zool A Ecol Genet Physiol. 2010 Apr 1;313(4):201-8. doi: 10.1002/jez.594. J Exp Zool A Ecol Genet Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20140952
-
The serotonin or dopamine by cyclic adenosine monophosphate-protein kinase A pathway involved in the agonistic behaviour of Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis.Physiol Behav. 2019 Oct 1;209:112621. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2019.112621. Epub 2019 Jul 16. Physiol Behav. 2019. PMID: 31323296
-
Mode of action of dopamine in inducing hyperglycemia in the fresh water edible crab, Oziothelphusa senex senex.J Exp Zool A Ecol Genet Physiol. 2014 Nov;321(9):531-9. doi: 10.1002/jez.1884. Epub 2014 Jul 30. J Exp Zool A Ecol Genet Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25074819
-
Effect of melatonin on hemolymph glucose and lactate levels in the fiddler crab Uca pugilator.J Exp Zool. 2001 Sep 1;290(4):379-83. doi: 10.1002/jez.1078. J Exp Zool. 2001. PMID: 11550185
-
Crustacean hyperglycemic hormone (CHH) neuropeptidesfamily: Functions, titer, and binding to target tissues.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2010 May 1;166(3):447-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2009.12.011. Epub 2009 Dec 22. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20026335 Review.
Cited by
-
CasEcR and CasMIH Genes in the Blue Crab, Callinectes sapidus: A Temporal Evaluation and Melatonin Effects.Front Physiol. 2022 Jun 21;13:903060. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.903060. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35800348 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin Uptake by Cells: An Answer to Its Relationship with Glucose?Molecules. 2018 Aug 10;23(8):1999. doi: 10.3390/molecules23081999. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30103453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative metabolomics analysis investigating the impact of melatonin-enriched diet on energy metabolism in the crayfish, Cherax destructor.J Comp Physiol B. 2023 Dec;193(6):615-630. doi: 10.1007/s00360-023-01518-0. Epub 2023 Oct 13. J Comp Physiol B. 2023. PMID: 37833417
-
Effects of miR-143 and its target receptor 5-HT2B on agonistic behavior in the Chinese mitten crab (Eriocheir sinensis).Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 24;11(1):4492. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83984-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33627750 Free PMC article.
-
Point-of-care testing for measuring haemolymph glucose in invertebrates is not a valid method.Conserv Physiol. 2019 Nov 28;7(1):coz079. doi: 10.1093/conphys/coz079. eCollection 2019. Conserv Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31798882 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balzer L., Espínola L. R., Fuentes-Pardo B. (1997). Daily variations of immunoreactive melatonin in the visual system of crayfish. Biol. Cell 89, 539–543. 10.1016/S0248-4900(98)80010-5 - DOI
-
- Camacho-Jiménez L., Díaz F., Muñoz-Márquez M. E., Farfán C., Re A. D., Ponce-Rivas E. (2017). Hyperglycemic and osmotic effects of dopamine and recombinant hormone CHH-B1 in the Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Mar. Freshwater Behav. Physiol. 50, 67–79. 10.1080/10236244.2017.1304155 - DOI
-
- Carroll N. V., Longley R. W., Roe J. H. (1956). The determination of glycogen in liver and muscle by use of anthrone reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 220, 583–593. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

