A Network Pharmacology Approach to Uncover the Multiple Mechanisms of Hedyotis diffusa Willd. on Colorectal Cancer
- PMID: 29619072
- PMCID: PMC5829364
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/6517034
A Network Pharmacology Approach to Uncover the Multiple Mechanisms of Hedyotis diffusa Willd. on Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
Background: As one of the most frequently diagnosed cancer diseases globally, colorectal cancer (CRC) remains an important cause of cancer-related death. Although the traditional Chinese herb Hedyotis diffusa Willd. (HDW) has been proven to be effective for treating CRC in clinical practice, its definite mechanisms have not been completely deciphered.
Objective: The aim of our research is to systematically explore the multiple mechanisms of HDW on CRC.
Methods: This study adopted the network pharmacology approach, which was mainly composed of active component gathering, target prediction, CRC gene collection, network analysis, and gene enrichment analysis.
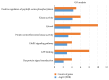
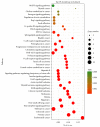
Results: The network analysis showed that 10 targets might be the therapeutic targets of HDW on CRC, namely, HRAS, PIK3CA, KRAS, TP53, APC, BRAF, GSK3B, CDK2, AKT1, and RAF1. The gene enrichment analysis implied that HDW probably benefits patients with CRC by modulating pathways related to cancers, infectious diseases, endocrine system, immune system, nervous system, signal transduction, cellular community, and cell motility.
Conclusions: This study partially verified and predicted the pharmacological and molecular mechanism of HDW against CRC from a holistic perspective, which will also lay a foundation for the further experimental research and clinical rational application of HDW.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

