The Role of the Level of Interleukin-33 in the Therapeutic Outcomes of Immunotherapy in Patients with Allergic Rhinitis
- PMID: 29619104
- PMCID: PMC5882380
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0037-1605596
The Role of the Level of Interleukin-33 in the Therapeutic Outcomes of Immunotherapy in Patients with Allergic Rhinitis
Abstract
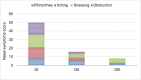
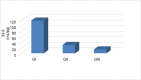
Introduction Allergic rhinitis (AR) affects up to 40% of the population and results in nasal itching, congestion, sneezing, and clear rhinorrhea. Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the changes in the clinical symptoms and in the level of serum interleukin (IL)-33 before and after pollen immunotherapy (IT) in patients with AR. Methods The total symptom score and the levels of total immunoglobulin E (IgE) and IL-33 were determined in the serum of 10 non-allergic healthy controls and 45 patients with AR who were equally divided into 3 groups: GI (patients did not receive IT), GII (patients had received IT for 6 months) and GIII (patients had received IT for 2 years). Results There was a significantly higher concentration of IgE and IL-33 in the serum of patients with AR than in that of non-allergic patients. Furthermore, serum level of IL-33 decreased significantly after pollen IT. But, there was no significant reduction in the serum level of IL-33 between GII and GIII patients. Conclusion Our results show a clinical improvement associated with a decrease in serum level of IL-33 after pollen IT.
Keywords: allergen immunotherapy; allergic rhinitis; helper T cells; immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Etiopathogenesis and management of perennial allergic rhinitis: a state-of-the-art review.Treat Respir Med. 2004;3(1):45-57. doi: 10.2165/00151829-200403010-00006. Treat Respir Med. 2004. PMID: 15174893 Review.
-
Cry j 1-induced synthesis of interleukin-5 and interferon-gamma by peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with seasonal allergic rhinitis due to Japanese cedar pollens.Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1998;538:143-51. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1998. PMID: 9879414
-
Some immunological aspects of patients with rhinitis in Lebanon.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2002 May;24(2):289-301. doi: 10.1081/iph-120003762. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2002. PMID: 12066854
-
The study of a possible correlation between serum levels of interleukin 17 and clinical severity in patients with allergic rhinitis.Allergy Rhinol (Providence). 2017 Oct 1;8(3):126-131. doi: 10.2500/ar.2017.8.0207. Allergy Rhinol (Providence). 2017. PMID: 29070269 Free PMC article.
-
[Rhinitis in adults].Acta Med Croatica. 2011;65(2):181-7. Acta Med Croatica. 2011. PMID: 22359885 Review. Croatian.
Cited by
-
Sublingual Immunotherapy in Allergic Rhinitis: Search for a Suitable Biomarker Continues!Indian J Pediatr. 2018 Oct;85(10):834-835. doi: 10.1007/s12098-018-2773-2. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Indian J Pediatr. 2018. PMID: 30128633 No abstract available.
-
Type 2 innate lymphoid cells participate in IL-33-stimulated Th2-associated immune response in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Oct;18(4):3109-3116. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7924. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31572551 Free PMC article.
-
The production, function, and clinical applications of IL-33 in type 2 inflammation-related respiratory diseases.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 5;15:1436437. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1436437. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39301028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Advances of IL-33/ST2 signaling pathway in allergic rhinitis].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Jun;34(6):565-568. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2020.06.020. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32842193 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Phase 2a randomized, placebo-controlled study of anti-IL-33 in peanut allergy.JCI Insight. 2019 Nov 14;4(22):e131347. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.131347. JCI Insight. 2019. PMID: 31723064 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Uzzaman A, Story R. Chapter 5: Allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2012;33 01:S15–S18. - PubMed
-
- Cox L, Wallace D. Specific allergy immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis: subcutaneous and sublingual. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2011;31(03):561–599. - PubMed
-
- Asaka D, Yoshikawa M, Nakayama T, Yoshimura T, Moriyama H, Otori N. Elevated levels of interleukin-33 in the nasal secretions of patients with allergic rhinitis. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2012;158 01:47–50. - PubMed
-
- Schatz M, Meltzer E O, Nathan R et al.Psychometric validation of the rhinitis control assessment test: a brief patient-completed instrument for evaluating rhinitis symptom control. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010;104(02):118–124. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials