A study of the key genes and inflammatory signaling pathways involved in HLA-B27-associated acute anterior uveitis families
- PMID: 29620146
- PMCID: PMC5979938
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3596
A study of the key genes and inflammatory signaling pathways involved in HLA-B27-associated acute anterior uveitis families
Abstract
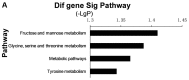
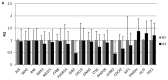
The present study was conducted to investigate the key genes and the inflammatory signaling pathways involved in HLA-B27-associated acute anterior uveitis (AAU) families. Four families with HLA-B27‑positive aau patients and their HLA-B27-positive blood relatives were included in the study. peripheral blood monocytes were isolated from the subjects and stimulated by lipopolysaccharides (LPS). Gene expression microarrays were used to identify the differentially expressed genes (DEGs), and the DEGs were analyzed by a range of bioinformatics-based techniques, including Gene Ontology (GO), Pathway analysis, Signal-Net analysis and Gene Relation Network (Gene-Rel-Net). Finally, ELISA was used to quantify cytokines in the supernatant. The gene expression microarrays identified 801 DEGs, including 349 upregulated and 452 downregulated genes. The GO analysis revealed several important functions, including metabolic, immune and inflammatory responses. The pathway analysis highlighted the enhanced activity of Staphylococcus aureus infection, chemokine and metabolic signaling pathways, as well as cytokine-to‑cytokine receptor interactions. A total of 18 DEGs that were found to play critical roles by Signal-Net and Gene-Rel-Net and verified by quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis were identified as key genes. In conclusion, monocytes from the AUU patients were more sensitive and exhibited a more prominent inflammatory response to stimulation by LPS compared with monocytes from healthy HLA-B27-positive blood relatives. These characterized DEGs may provide new evidence for the pathogenesis of AAU and help identify new therapeutic targets.
Figures








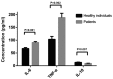
References
-
- Jabs DA, Nussenblatt RB, Rosenbaum JT, Standardization of Uveitis Nomenclature (SUN) Working Group Standardization of uveitis nomenclature for reporting clinical data. Results of the First International Workshop. Am J Ophthalmol. 2005;140:509–516. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2005.03.057. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

