Bone marrow‑derived mesenchymal stem cell‑conditioned medium attenuates tubulointerstitial fibrosis by inhibiting monocyte mobilization in an irreversible model of unilateral ureteral obstruction
- PMID: 29620281
- PMCID: PMC5983967
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2018.8848
Bone marrow‑derived mesenchymal stem cell‑conditioned medium attenuates tubulointerstitial fibrosis by inhibiting monocyte mobilization in an irreversible model of unilateral ureteral obstruction
Abstract
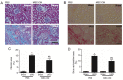
Mesenchymal stem cell‑conditioned medium (MSC‑CM) contains various cytokines (osteopontin and macrophage colony stimulating factor 1) secreted by MSCs and may modulate the immune response in tubulointerstitial fibrosis. The aim of the present study was to investigate whether MSC‑CM treatment may affect B cell‑dependent immune responses, which have previously been reported to facilitate the renal fibrotic processes following unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO). In the present study, histological analysis, flow cytometry, western blotting and reverse transcription‑quantitative polymerase chain reaction were performed. MSC‑CM treatment was observed to impede renal infiltration of B lymphocytes and the expression of CC chemokine ligand‑2. Additionally, UUO suppressed the subsequent recruitment of monocytes/macrophages to the kidney, limited local inflammation and attenuated renal fibrosis. The findings of the present study identified a potential mechanism of MSC‑CM in ameliorating the UUO‑kidney.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

