Intraocular inflammation in a case of bee sting injury
- PMID: 29623252
- PMCID: PMC5854761
- DOI: 10.3205/oc000084
Intraocular inflammation in a case of bee sting injury
Abstract
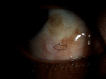
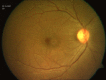
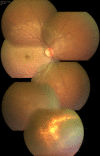
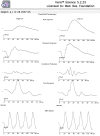
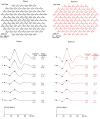
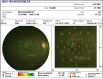
A19-year-old man presented with decreased vision in the right eye following a bee sting injury, ten days back. Examination revealed conjunctival hyperemia at the site of the sting, anterior uveitis, vitritis, mild disc hyperemia, ocular hypotony, and striae at macula. Treatment was initiated elsewhere with topical antibiotics, steroid, and cycloplegic. Systemic steroids were added. Three weeks later, vitiritis resolved, intraocular pressure became normal and the vision improved from 20/60 to 20/20. However, a chorioretinal atrophy in the vicinity of the sting site was noted. Global electroretinogram (ERG) revealed reduced scotopic responses and depressed oscillatory potentials; even though the photopic response was normal. Multifocal ERG and microperimetry were normal. Two months later, after discontinuation of medication, a traumatic mydriasis with a sluggish pupillary reaction was noted. Sixteen months later, the fundus remained stable. This is a rare case report of a bee sting injury leading to anterior uveitis, vitritis, and cilio-choroidal detachment, mimicking endophthalmitis. Timely recognition of the cause of the intraocular inflammation and appropriate treatment led to optimal recovery.
Keywords: bee sting; choroidal detachment; pupil; uveitis; vitritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Chen CJ, Richardson CD. Bee sting-induced ocular changes. Ann Ophthalmol. 1986 Oct;18(10):285–286. - PubMed
-
- Al-Towerki AE. Corneal honeybee sting. Cornea. 2003 Oct;22(7):672–674. doi: 10.1097/00003226-200310000-00011. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00003226-200310000-00011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Singh I, Chaudhary U. Bilateral optic neuritis following multiple wasp stings. J Indian Med Assoc. 1986 Aug;84(8):251–252. - PubMed
-
- Song HS, Wray SH. Bee sting optic neuritis. A case report with visual evoked potentials. J Clin Neuroophthalmol. 1991 Mar;11(1):45–49. - PubMed
-
- Berríos RR, Serrano LA. Bilateral optic neuritis after a bee sting. Am J Ophthalmol. 1994 May;117(5):677–678. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9394(14)70084-4. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9394(14)70084-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

