Excessive Pretreatment Weight Loss Is a Risk Factor for the Survival Outcome of Esophageal Carcinoma Patients Undergoing Radical Surgery and Postoperative Adjuvant Chemotherapy
- PMID: 29623265
- PMCID: PMC5830280
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/6075207
Excessive Pretreatment Weight Loss Is a Risk Factor for the Survival Outcome of Esophageal Carcinoma Patients Undergoing Radical Surgery and Postoperative Adjuvant Chemotherapy
Abstract
Background: The prognostic values of weight loss and body mass index (BMI) in esophageal carcinoma remain controversial. This study aimed to evaluate the impacts of weight loss on the survival of patients undergoing radical surgery and adjuvant chemotherapy.
Methods: The medical records of 189 consecutive patients with nonmetastatic esophageal carcinoma treated in our hospital between January 2012 and December 2013 were reviewed, and 121 patients were included for analysis.
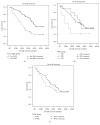
Results: Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed that the 3-year overall survival rate was significantly higher in the low pretreatment weight loss (pre-LWL) group than in the high pretreatment weight loss (pre-HWL) group (P < 0.001). In addition, the 3-year overall survival rate of normal weight group was higher than that of overweight and underweight groups (P = 0.007). Multivariate Cox proportional hazards analysis showed that pre-LWL group had a significantly better 3-year overall survival than pre-HWL group (P = 0.027, HR = 1.89, and 95% CI = 1.07-3.32). pN stage and age were also the survival prognostic factors.
Conclusions: Our study showed that low pretreatment weight loss predicted a better survival outcome in the esophageal carcinoma patients with radical surgery and adjuvant chemotherapy. However, BMI and weight loss during treatment had no impact on the survival outcome.
Figures
References
-
- Herszényi L., Tulassay Z. Epidemiology of gastrointestinal and liver tumors. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences. 2010;14(4):249–258. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

