The Cost of Patients with Chronic Kidney Failure Before Dialysis: Results from the IRIDE Observational Study
- PMID: 29623638
- PMCID: PMC6249198
- DOI: 10.1007/s41669-017-0062-z
The Cost of Patients with Chronic Kidney Failure Before Dialysis: Results from the IRIDE Observational Study
Abstract
Background: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is an important public health problem. Most of the evidence on its costs relates to patients receiving dialysis or kidney transplants, which shows that, in these phases, CKD poses a high burden to payers. Less evidence is available on the costs of the predialytic phase.
Objective: The aim of this study was to estimate the annual cost of patients with CKD not receiving dialysis treatment, using the Italian healthcare system perspective and a prospective approach.
Methods: A 3-year observational study (December 2010-September 2014) was carried out to collect data on resource consumption for 864 patients with CKD. Costs were estimated for both patients who completed the follow-up and dropouts.
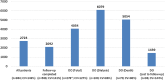
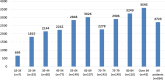
Results: The mean annual total (healthcare) cost per patient equalled €2723 (95% confidence interval 2463.0-2983.3). Disease severity (higher CKD stage), multiple comorbidities, dropout status and belonging to the southern region are predictive of higher costs. Pharmaceuticals, hospitalisation, and outpatient services account for 71.5, 18.8 and 9.7% of total healthcare expenditure, respectively. Recent estimates of Italian costs of patients receiving dialysis are nine times the unit costs of CKD for patients estimated in this study. Unit costs at stage 5 CKD (the highest level of severity) equals 4.7 times the costs for patients at stage 1 CKD.
Conclusion: Despite its limitations, this study provides further evidence on the opportunity to invest in the first phases of CKD to avoid progression and an increase in healthcare costs.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
Umberto di Luzio Paparatti is an Abbvie employee and may own Abbvie stock/options. Anna Maria Costanzo was an Abbvie employee at the time the study was conducted and may own stock/options. Claudio Jommi, Patrizio Armeni, Margherita Battista, Paolo Di Procolo, Giuseppe Conte, Claudio Ronco, Mario Cozzolino, Gabriella Concas and Giuseppe Remuzzi declare that thay have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Chronic kidney disease initiative—protecting kidney health. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2015. http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/projects/pdfs/ckd_summary.pdf. Accessed 31 Oct 2017.
-
- Cicchetti A, Ruggeri M, Codella P, Ridolfi A. I costi socio- sanitari dell’insufficienza renale cronica. Farmeconomia e Percorsi Terapeutici. 2011;12(1):21–28. doi: 10.7175/fe.v12i1.95. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources