Human Hippocampal Neurogenesis Persists throughout Aging
- PMID: 29625071
- PMCID: PMC5957089
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.03.015
Human Hippocampal Neurogenesis Persists throughout Aging
Abstract
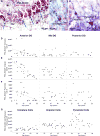
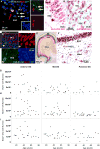
Adult hippocampal neurogenesis declines in aging rodents and primates. Aging humans are thought to exhibit waning neurogenesis and exercise-induced angiogenesis, with a resulting volumetric decrease in the neurogenic hippocampal dentate gyrus (DG) region, although concurrent changes in these parameters are not well studied. Here we assessed whole autopsy hippocampi from healthy human individuals ranging from 14 to 79 years of age. We found similar numbers of intermediate neural progenitors and thousands of immature neurons in the DG, comparable numbers of glia and mature granule neurons, and equivalent DG volume across ages. Nevertheless, older individuals have less angiogenesis and neuroplasticity and a smaller quiescent progenitor pool in anterior-mid DG, with no changes in posterior DG. Thus, healthy older subjects without cognitive impairment, neuropsychiatric disease, or treatment display preserved neurogenesis. It is possible that ongoing hippocampal neurogenesis sustains human-specific cognitive function throughout life and that declines may be linked to compromised cognitive-emotional resilience.
Keywords: Ki-67; NeuN; PSA-NCAM; Sox2; dentate gyrus; doublecortin; granule cells; nestin; neural progenitor; volume.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Adult Human Hippocampal Neurogenesis: Controversy and Evidence.Trends Mol Med. 2018 Jun;24(6):521-522. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2018.04.002. Epub 2018 Apr 23. Trends Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29699864
-
Does Adult Neurogenesis Persist in the Human Hippocampus?Cell Stem Cell. 2018 Dec 6;23(6):780-781. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.11.006. Cell Stem Cell. 2018. PMID: 30526879 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Considerations for Assessing the Extent of Hippocampal Neurogenesis in the Adult and Aging Human Brain.Cell Stem Cell. 2018 Dec 6;23(6):782-783. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.10.025. Cell Stem Cell. 2018. PMID: 30526880 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ben Abdallah NM, Slomianka L, Lipp HP. Reversible effect of X-irradiation on proliferation, neurogenesis, and cell death in the dentate gyrus of adult mice. Hippocampus. 2007;17:1230–1240. - PubMed
-
- Bergmann O, Liebl J, Bernard S, Alkass K, Yeung MS, Steier P, Kutschera W, Johnson L, Landén M, Druid H, et al. The age of olfactory bulb neurons in humans. Neuron. 2012;74:634–639. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

