Case report: lactic acidosis and rhabdomyolysis during telbivudine and tenofovir treatment for chronic hepatitis B
- PMID: 29625557
- PMCID: PMC5889588
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-018-0773-3
Case report: lactic acidosis and rhabdomyolysis during telbivudine and tenofovir treatment for chronic hepatitis B
Abstract
Background: Current treatment options for chronic hepatitis B (CHB) are pegylated interferon alpha and nucleoside analogues (NAs). NAs have relatively fewer side effects than interferon alpha, and generally well tolerated. Previously 12.9% of patients on telbivudine treatment were reported to develop severe elevation of serum creatine phosphokinase (CPK) levels, but related clinical disease, like lactic acidosis (LA) and rhabdomyolysis (RM) were rare. The pathophysiology may be mitochondrial toxicity, for the NAs inhibit not only hepatitis B virus (HBV) polymerase, but also the host mitochondrial DNA polymerase γ. As mitochondria are the main sites of oxidative phosphorylation, there will be an increase of pyruvate reduction to lactic acid and insufficient adenosine triphosphate. The accumulation of lactic acid causes LA, while lack of energy leads to cell dysfunction and mitochondria-associated disease, including RM. All five NAs, except tenofovir, have been reported causing LA and RM. Here we report the first case of CHB patients developing fatal LA and RM during telbivudine and tenofovir treatment.
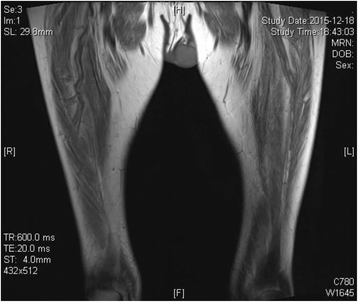
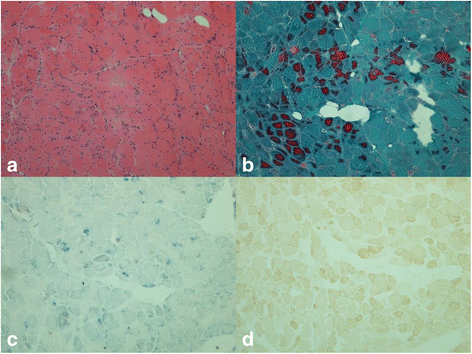
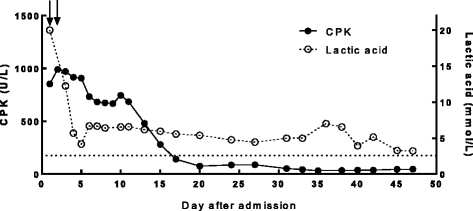
Case presentation: The patient is a 51-year-old man who was hospitalized in November 2015. He had taken telbivudine regularly because of CHB. Later, tenofovir was added to antiviral treatment because of HBV resistance. Then he had myalgia, chest tightness and anorexia. The blood lactate was 12.7 mmol/L. The arterial blood gas analysis showed pH 7.25, base excess 21.1 mmol/L. CPK was 991 U/L, myoglobin was 1745 ng/ml and creatine was 83 μmol/L. Abdomen magnetic resonance revealed cirrhosis. Muscle biopsy revealed myogenic lesion with abnormality of mitochondria and fat metabolism. The patient was diagnosed with Hepatitis B envelope Antigen positive CHB, cirrhosis, LA and RM characterized by myalgia and elevated myoglobin. He was given tenofovir alone as antiviral treatment instead. After hemodialysis and 4 weeks` treatment of corticosteroids, his symptoms recovered, and blood lactate gradually returned to a normal range.
Conclusions: This case shows that tenofovir may trigger muscle damage and fatal RM in combination with telbivudine treatment in CHB patients. Thus, patients receiving tenofovir and telbivudine should be closely monitored for muscular abnormalities, blood lactate level and other mitochondrial toxicity associated side effects.
Keywords: Lactic acidosis; Mitochondrial toxicity; Myopathy; Rhabdomyolysis; Telbivudine; Tenofovir.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Written informed consent to participate in the study from the patient was obtained.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication from the patient was obtained.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Telbivudine-induced rhabdomyolysis in a patient undergoing haemodialysis: A case report and review of literature.J Int Med Res. 2023 Dec;51(12):3000605231222244. doi: 10.1177/03000605231222244. J Int Med Res. 2023. PMID: 38140948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rhabdomyolysis, lactic acidosis, and multiple organ failure during telbivudine treatment for hepatitis B: a case report and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2017 Nov 27;11(1):331. doi: 10.1186/s13256-017-1498-6. J Med Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 29179767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lactic acidosis during telbivudine treatment for HBV: a case report and literature review.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Sep 7;19(33):5575-80. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i33.5575. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 24023503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extrahepatic effects of nucleoside and nucleotide analogues in chronic hepatitis B treatment.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014 Mar;29(3):428-34. doi: 10.1111/jgh.12499. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24372662 Review.
-
Continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration for hyperlactatemia caused by telbivudine in a patient with chronic hepatitis B: a case report and update review.J Dig Dis. 2015 Mar;16(3):164-7. doi: 10.1111/1751-2980.12173. J Dig Dis. 2015. PMID: 25043654 Review.
Cited by
-
Severe lactic acidosis during tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and cobicistat combination for HIV patient.BMJ Case Rep. 2023 Nov 3;16(11):e255751. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2023-255751. BMJ Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 37923339
-
Telbivudine-induced rhabdomyolysis in a patient undergoing haemodialysis: A case report and review of literature.J Int Med Res. 2023 Dec;51(12):3000605231222244. doi: 10.1177/03000605231222244. J Int Med Res. 2023. PMID: 38140948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Creatine kinase elevation in chronic hepatitis B patients with telbivudine therapy: influence of telbivudine plasma concentration and single nucleotide polymorphisms of TK2, RRM2B, and NME4.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2024 Jul;80(7):1029-1038. doi: 10.1007/s00228-024-03674-w. Epub 2024 Mar 19. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38502357
-
Telbivudine-Induced Myopathy: Clinical Features, Histopathological Characteristics, and Risk Factors.J Clin Neurol. 2023 Jan;19(1):52-59. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2023.19.1.52. J Clin Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36606646 Free PMC article.
-
Severe Lactic Acidosis Due to Acute Intoxication by Emtricitabine/Tenofovir Alafenamide.Cureus. 2021 Oct 24;13(10):e19008. doi: 10.7759/cureus.19008. eCollection 2021 Oct. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34824925 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liaw YF, Gane E, Leung N, Zeuzem S, Wang Y, Lai CL, Heathcote EJ, Manns M, Bzowej N, Niu J, Han SH, Hwang SG, Cakaloglu Y, Tong MJ, Papatheodoridis G, Chen Y, Brown NA, Albanis E, Galil K, Naoumov NV, GLOBE Study Group 2-Year GLOBE trial results: telbivudine is superior to lamivudine in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Gastroenterology. 2009;136(2):486–495. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.10.026. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chan HL, Chen YC, Gane EJ, Sarin SK, Suh DJ, Piratvisuth T, Prabhakar B, Hwang SG, Choudhuri G, Safadi R. Randomized clinical trial: efficacy and safety of telbivudine and lamivudine in treatment-naïve patients with HBV-related decompensated cirrhosis. J Viral Hepat. 2012;19:732–743. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2893.2012.01600.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

