Sulfotransferase 4A1 Increases Its Expression in Mouse Neurons as They Mature
- PMID: 29626075
- PMCID: PMC5931435
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.118.080838
Sulfotransferase 4A1 Increases Its Expression in Mouse Neurons as They Mature
Abstract
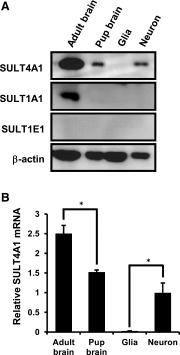
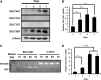
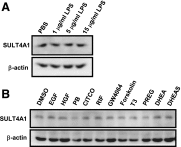
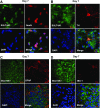
Cytosolic sulfotransferases (SULTs) catalyze sulfation and play essential roles in detoxification of xenobiotics as well as inactivation of endobiotics. SULT4A1, which was originally isolated as a brain-specific sulfotransferase, is the most highly conserved isoform among SULTs in vertebrates. Here, expression of SULT4A1 was examined neuron enriched and neuron-glia mixed cells derived from mouse embryo brains at day 14 gestation and mixed glia from 2-day-old neonate brains. Western blots showed an increase of SULT4A1 expression as neurons maturated. Reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction and agarose gel analysis found two different forms (variant and wild type) of SULT4A1 mRNA in neurons; the level of wild type correlated with the protein level of SULT4A1. SULT1E1 was not expressed in mouse brains, neuron-enriched cells, or mixed glia cells. SULT1A1 protein was only detected in adult brains. Immunofluorescence staining of neuron-glia mixed cells confirmed selective expression of SULT4A1 in neurons, including dopaminergic neurons, but not in either astrocytes or microglia. Thus, SULT4A1 is a neuron-specific sulfotransferase and may play a role in neuronal development.
U.S. Government work not protected by U.S. copyright.
Figures
References
-
- Block ML, Hong JS. (2005) Microglia and inflammation-mediated neurodegeneration: multiple triggers with a common mechanism. Prog Neurobiol 76:77–98. - PubMed
-
- Falany CN, Krasnykh V, Falany JL. (1995) Bacterial expression and characterization of a cDNA for human liver estrogen sulfotransferase. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 52:529–539. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

