Pelvic Artery Embolization for Treatment of Postpartum Hemorrhage
- PMID: 29628615
- PMCID: PMC5886774
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0038-1636520
Pelvic Artery Embolization for Treatment of Postpartum Hemorrhage
Abstract
Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is the leading cause of maternal perinatal morbidity and mortality worldwide. Defined as greater than 500 mL blood loss after vaginal delivery, and greater than 1,000 mL blood loss after cesarean delivery, PPH has many causes, including uterine atony, lower genital tract lacerations, coagulopathy, and placental anomalies. Correction of coagulopathy and identification of the cause of bleeding are mainstays of treatment. Medical therapies such as uterotonics, balloon tamponade, pelvic artery embolization, and uterine-sparing surgical options are available. Hysterectomy is performed when conservative therapies fail. Pelvic artery embolization is safe and effective, and is the first-line therapy for medically refractory PPH. A thorough knowledge of pelvic arterial anatomy is critical. Recognition of variant anatomy can prevent therapeutic failure. Pelvic embolization is minimally invasive, has a low complication rate, spares the uterus, and preserves fertility.
Keywords: embolization; fertility; interventional radiology; postpartum hemorrhage; uterine artery.
Figures
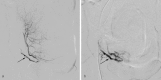
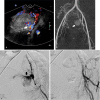
Similar articles
-
Uterine Artery Embolization for Primary Postpartum Hemorrhage.Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2021 Mar;24(1):100727. doi: 10.1016/j.tvir.2021.100727. Epub 2021 Apr 16. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2021. PMID: 34147194 Review.
-
Postpartum Hemorrhage.Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017 Dec;20(4):266-273. doi: 10.1053/j.tvir.2017.10.007. Epub 2017 Oct 10. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017. PMID: 29224660 Review.
-
Success Rate and Long-Term Effects of Embolization of Pelvic Arteries for the Treatment of Postpartum Hemorrhage.Transfus Med Hemother. 2023 Feb 21;50(3):226-233. doi: 10.1159/000527614. eCollection 2023 Jun. Transfus Med Hemother. 2023. PMID: 37434998 Free PMC article.
-
Uterine balloon tamponade for the treatment of postpartum hemorrhage: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Apr;222(4):293.e1-293.e52. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2019.11.1287. Epub 2020 Jan 6. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020. PMID: 31917139
-
Laparoscopic Ligation of Uterine Vasculature for Fertility-Sparing Management of Postabortal Hemorrhage.J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019 Jan;26(1):36-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jmig.2018.03.020. Epub 2018 Mar 30. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 2019. PMID: 29609031
Cited by
-
The Emergent Pelvic Artery Embolization in the Management of Postpartum Hemorrhage: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2021 Apr;76(4):234-244. doi: 10.1097/OGX.0000000000000887. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2021. PMID: 33908615 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy of uterine artery embolization for postpartum hemorrhage with placenta accreta spectrum disorder: clinical outcomes in a cohord of 112 pregnant women.Eur Radiol. 2025 Jun 13. doi: 10.1007/s00330-025-11744-5. Online ahead of print. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40512219
-
Primary and secondary postpartum haemorrhage: a review for a rationale endovascular approach.CVIR Endovasc. 2024 Feb 13;7(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s42155-024-00429-7. CVIR Endovasc. 2024. PMID: 38349501 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Animal models of postpartum hemorrhage.Lab Anim (NY). 2024 Apr;53(4):93-106. doi: 10.1038/s41684-024-01349-8. Epub 2024 Mar 25. Lab Anim (NY). 2024. PMID: 38528231 Review.
-
Effect of Uterine Artery Ligation and Uterine Artery Embolization on Postpartum Hemorrhage Due to Uterine Asthenia after Cesarean Section and Its Effect on Blood Flow and Function of Uterine and Ovarian Arteries.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Mar 21;2022:1337234. doi: 10.1155/2022/1337234. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. Retraction in: J Healthc Eng. 2023 Sep 27;2023:9848967. doi: 10.1155/2023/9848967. PMID: 35356624 Free PMC article. Retracted. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Say L, Chou D, Gemmill A et al.Global causes of maternal death: a WHO systematic analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2014;2(06):e323–e333. - PubMed
-
- Devine P C. Obstetric hemorrhage. Semin Perinatol. 2009;33(02):76–81. - PubMed
-
- WHO.WHO Recommendations for the Prevention and Treatment of Postpartum Haemorrhage Geneva: World Health Organisation; 2012 - PubMed
-
- WHO, UNFPA, The World Bank. Trends in Maternal Mortality: 1990 to 2010 - WHO, UNICEF, UNFPA and the World Bank Estimates;2012
-
- Kumar N. Postpartum hemorrhage; a major killer of woman: review of current scenario. Obstet Gynecol Int J. 2016;4(04):116.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

