Management of growth arrest: Current practice and future directions
- PMID: 29628701
- PMCID: PMC5883917
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcot.2018.01.001
Management of growth arrest: Current practice and future directions
Abstract
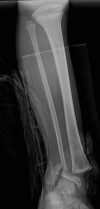
Introduction: Premature growth arrest can pose a challenge to the orthopedic surgeon. Various options for treating physeal arrest exist.
Methods: Systematic searches were conducted on PubMed/Medline, ScienceDirect, OVID, and Cochrane Library. Secondary searching was performed, where certain articles from reference lists of the selected studies were reviewed that were not found in the primary search.
Results: This review article discusses the different methods of management for premature growth arrest.
Conclusions: The use of mesenchymal stem cells provides a promising alternative treatment modality.
Keywords: Chondrodiastasis; Deformity correction; Epiphysiodesis; Growth arrest; Physeal bar; Physeal injuries.
Figures





References
-
- Mizuta T., Benson W.M., Foster B.K., Morris L.L. Statistical analysis of the incidence of physeal injuries. J Pediatric Orthopaedics. 1987;7(5):518–523. - PubMed
-
- Mann D.C., Rajmaira S. Distribution of physeal and nonphyseal fractures in 2650 long-bone fractures in children aged 0–16 years. J Pediatric Orthopaedics. 1990;10(6):713–716. - PubMed
-
- Ogden J.A. Injury to the growth mechanisms of the immature skeleton. Skeletal Radiol. 1981;6(4):237–253. - PubMed
-
- Robert R.S. Informa Healthcare; United States: 2006. Limb Lengthening and Reconstruction Surgery. Chapter 32 Growth Arrest.
-
- Micheli L.J. 12 pediatric and adolescent sports injuries. Exercise Sport Sci Rev. 1986;14:359–374. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

