Hydrogen peroxide-triggered gene silencing in mammalian cells through boronated antisense oligonucleotides
- PMID: 29629168
- PMCID: PMC5875086
- DOI: 10.1039/c7sc04318j
Hydrogen peroxide-triggered gene silencing in mammalian cells through boronated antisense oligonucleotides
Abstract
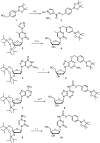
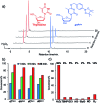
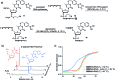
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is a reactive oxygen species (ROS) involved in various diseases, including neurodegeneration, diabetes, and cancer. Here, we introduce a new approach to use H2O2 to modulate specific gene expression in mammalian cells. H2O2-responsive nucleoside analogues, in which the Watson-Crick faces of the nucleobases are caged by arylboronate moieties, were synthesized. One of these analogues, boronated thymidine (dTB ), was incorporated into oligodeoxynucleotides (ODNs) using an automated DNA synthesizer. The hybridization ability of this boronated ODN to complementary RNA was clearly switched in the off-to-on direction upon H2O2 addition. Furthermore, we demonstrated H2O2-triggered gene silencing in mammalian cells using antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) modified with dTB . Our approach can be used for the regulation of any gene of interest by the sequence design of boronated ASOs and will contribute to the development of targeted disease therapeutics.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Estimated number of off-target candidate sites for antisense oligonucleotides in human mRNA sequences.Genes Cells. 2018 Jun;23(6):448-455. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12587. Epub 2018 Apr 18. Genes Cells. 2018. PMID: 29667281
-
Nonsense-mediated decay as a terminating mechanism for antisense oligonucleotides.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 May;42(9):5871-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku184. Epub 2014 Mar 3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24589581 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of 4'-C-(Aminoethyl)thymidine and 4'-C-[(N-Methyl)aminoethyl] Thymidine Nucleosides to Enhance DNA Stability.Curr Protoc. 2022 Sep;2(9):e501. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.501. Curr Protoc. 2022. PMID: 36073858
-
Does antisense make sense in dermatology?Acta Derm Venereol. 2001 Nov-Dec;81(6):385-91. doi: 10.1080/000155501317208282. Acta Derm Venereol. 2001. PMID: 11859937 Review.
-
The therapeutic potential of antisense oligonucleotides.Bioessays. 1995 Dec;17(12):1055-63. doi: 10.1002/bies.950171210. Bioessays. 1995. PMID: 8634067 Review.
Cited by
-
Selective inhibition of cancer cell migration using a pH-responsive nucleobase-modified DNA aptamer.Chem Sci. 2024 Sep 24;15(41):17097-102. doi: 10.1039/d4sc04424j. Online ahead of print. Chem Sci. 2024. PMID: 39355222 Free PMC article.
-
Amplified Production of a DNA Decoy Catalyzed by Intracellular MicroRNA.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025 Apr 7;64(15):e202424421. doi: 10.1002/anie.202424421. Epub 2025 Feb 11. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025. PMID: 39901657 Free PMC article.
-
Delivery of antisense oligonucleotide using polyethylenimine-based lipid nanoparticle modified with cell penetrating peptide.Drug Deliv. 2019 Dec;26(1):965-974. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2019.1667453. Drug Deliv. 2019. PMID: 31544540 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical synthesis of stimuli-responsive guide RNA for conditional control of CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing.Chem Sci. 2021 May 18;12(29):9934-9945. doi: 10.1039/d1sc01194d. eCollection 2021 Jul 28. Chem Sci. 2021. PMID: 34377390 Free PMC article.
-
Photocontrol of CRISPR/Cas9 function by site-specific chemical modification of guide RNA.Chem Sci. 2020 Sep 25;11(42):11478-11484. doi: 10.1039/d0sc04343e. Chem Sci. 2020. PMID: 34094391 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

