Insight into the Significance of Aspergillus fumigatus cyp51A Polymorphisms
- PMID: 29632011
- PMCID: PMC5971592
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00241-18
Insight into the Significance of Aspergillus fumigatus cyp51A Polymorphisms
Abstract
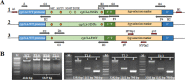
Triazole antifungal compounds are the first treatment choice for invasive aspergillosis. However, in the last decade the rate of azole resistance among Aspergillus fumigatus strains has increased notoriously. The main resistance mechanisms are well defined and mostly related to point mutations of the azole target, 14-α sterol demethylase (cyp51A), with or without tandem repeat integrations in the cyp51A promoter. Furthermore, different combinations of five Cyp51A mutations (F46Y, M172V, N248T, D255E, and E427K) have been reported worldwide in about 10% of all A. fumigatus isolates tested. The azole susceptibility profile of these strains shows elevated azole MICs, although on the basis of the azole susceptibility breakpoints, these strains are not considered azole resistant. The purpose of the study was to determine whether these cyp51A polymorphisms (single nucleotide polymorphisms [SNPs]) are responsible for the azole susceptibility profile and whether they are reflected in a poorer azole treatment response in vivo that could compromise patient treatment and outcome. A mutant with a cyp51A deletion was generated and became fully susceptible to all azoles tested. Also, three cyp51A gene constructions with different combinations of SNPs were generated and reintroduced into an azole-susceptible wild-type (WT) strain (the ΔakuBKU80 strain). The alternative model host Galleria mellonella was used to compare the virulence and voriconazole response of G. mellonella larvae infected with A. fumigatus strains with WT cyp51A or cyp51A with SNPs. All strains were pathogenic in G. mellonella larvae, although they did not respond similarly to voriconazole therapeutic doses. Finally, the full genomes of these strains were sequenced and analyzed in comparison with those of A. fumigatus WT strains, revealing that they belong to different strain clusters or lineages.
Keywords: Aspergillus fumigatus; Galleria mellonella; azole resistance; cyp51A polymorphisms; whole-genome sequencing.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Azole preexposure affects the Aspergillus fumigatus population in patients.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Sep;56(9):4948-50. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05990-11. Epub 2012 Jun 18. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22710122 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic perspective of triazole resistance in clinical and environmental Aspergillus fumigatus isolates without cyp51A mutations.Fungal Genet Biol. 2019 Nov;132:103265. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2019.103265. Epub 2019 Aug 26. Fungal Genet Biol. 2019. PMID: 31465846
-
Azole resistance profile of amino acid changes in Aspergillus fumigatus CYP51A based on protein homology modeling.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010 Jun;54(6):2425-30. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01599-09. Epub 2010 Apr 12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010. PMID: 20385860 Free PMC article.
-
Azole resistant Aspergillus fumigatus: an emerging problem.Med Mal Infect. 2013 Apr;43(4):139-45. doi: 10.1016/j.medmal.2013.02.010. Epub 2013 Apr 4. Med Mal Infect. 2013. PMID: 23562488 Review.
-
Exploring azole antifungal drug resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus with special reference to resistance mechanisms.Future Microbiol. 2014;9(5):697-711. doi: 10.2217/fmb.14.27. Future Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24957095 Review.
Cited by
-
In Vivo Selection of a Unique Tandem Repeat Mediated Azole Resistance Mechanism (TR120) in Aspergillus fumigatus cyp51A, Denmark.Emerg Infect Dis. 2019 Mar;25(3):577-580. doi: 10.3201/eid2503.180297. Emerg Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30789127 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic Distribution of csp1 Types in Aspergillus fumigatus and Their Correlates to Azole Antifungal Drug Resistance.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Dec 22;9(3):e0121421. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.01214-21. Epub 2021 Nov 17. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34787484 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic and Molecular Identification of Genes Contributing to the Caspofungin Paradoxical Effect in Aspergillus fumigatus.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Oct 26;10(5):e0051922. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00519-22. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36094204 Free PMC article.
-
cyp51A Mutations, Extrolite Profiles, and Antifungal Susceptibility in Clinical and Environmental Isolates of the Aspergillus viridinutans Species Complex.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Oct 22;63(11):e00632-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00632-19. Print 2019 Nov. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31451501 Free PMC article.
-
Azole Resistance in Veterinary Clinical Aspergillus fumigatus Isolates in the Netherlands.Mycopathologia. 2024 Jun 12;189(4):50. doi: 10.1007/s11046-024-00850-5. Mycopathologia. 2024. PMID: 38864903 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Taccone FS, Van den Abeele AM, Bulpa P, Misset B, Meersseman W, Cardoso T, Paiva JA, Blasco-Navalpotro M, De Laere E, Dimopoulos G, Rello J, Vogelaers D, Blot SI, AspICU Study Investigators. 2015. Epidemiology of invasive aspergillosis in critically ill patients: clinical presentation, underlying conditions, and outcomes. Crit Care 19:7. doi:10.1186/s13054-014-0722-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

