Translation initiation in bacterial polysomes through ribosome loading on a standby site on a highly translated mRNA
- PMID: 29632209
- PMCID: PMC5924895
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1718029115
Translation initiation in bacterial polysomes through ribosome loading on a standby site on a highly translated mRNA
Abstract
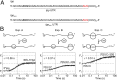
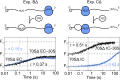
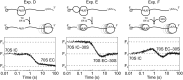
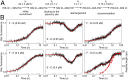
During translation, consecutive ribosomes load on an mRNA and form a polysome. The first ribosome binds to a single-stranded mRNA region and moves toward the start codon, unwinding potential mRNA structures on the way. In contrast, the following ribosomes can dock at the start codon only when the first ribosome has vacated the initiation site. Here we show that loading of the second ribosome on a natural 38-nt-long 5' untranslated region of lpp mRNA, which codes for the outer membrane lipoprotein from Escherichia coli, takes place before the leading ribosome has moved away from the start codon. The rapid formation of this standby complex depends on the presence of ribosomal proteins S1/S2 in the leading ribosome. The early recruitment of the second ribosome to the standby site before translation by the leading ribosome and the tight coupling between translation elongation by the first ribosome and the accommodation of the second ribosome can contribute to high translational efficiency of the lpp mRNA.
Keywords: global fitting; polysome formation; ribosome; translation initiation; translational efficiency.
Copyright © 2018 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structured mRNAs regulate translation initiation by binding to the platform of the ribosome.Cell. 2007 Sep 21;130(6):1019-31. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.07.008. Cell. 2007. PMID: 17889647
-
Role of Ribosomal Protein bS1 in Orthogonal mRNA Start Codon Selection.Biochemistry. 2025 Feb 4;64(3):710-718. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.4c00688. Epub 2025 Jan 24. Biochemistry. 2025. PMID: 39854700 Free PMC article.
-
Stem-Loop Structures within mRNA Coding Sequences Activate Translation Initiation and Mediate Control by Small Regulatory RNAs.Mol Cell. 2017 Oct 5;68(1):158-170.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.08.015. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Mol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28918899
-
Dealing with stable structures at ribosome binding sites: bacterial translation and ribosome standby.RNA Biol. 2007 Nov;4(3):113-7. doi: 10.4161/rna.4.3.5350. Epub 2007 Nov 29. RNA Biol. 2007. PMID: 18094628 Review.
-
A salvage pathway for protein structures: tmRNA and trans-translation.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2003;57:101-23. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.57.030502.090945. Epub 2003 May 1. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12730326 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of spatial heterogeneity on bacterial genetic circuits.PLoS Comput Biol. 2020 Sep 14;16(9):e1008159. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008159. eCollection 2020 Sep. PLoS Comput Biol. 2020. PMID: 32925923 Free PMC article.
-
Light-inducible expression of translation factor EF-Tu during acclimation to strong light enhances the repair of photosystem II.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Oct 15;116(42):21268-21273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1909520116. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31570574 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation outside the box: New mechanisms for small RNAs.Mol Microbiol. 2020 Sep;114(3):363-366. doi: 10.1111/mmi.14523. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Mol Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32367584 Free PMC article.
-
5'UTR G-quadruplex structure enhances translation in size dependent manner.Nat Commun. 2024 May 10;15(1):3963. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48247-8. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38729943 Free PMC article.
-
Translational Control by Ribosome Pausing in Bacteria: How a Non-uniform Pace of Translation Affects Protein Production and Folding.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jan 11;11:619430. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.619430. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33505387 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

