Heritability enrichment of specifically expressed genes identifies disease-relevant tissues and cell types
- PMID: 29632380
- PMCID: PMC5896795
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-018-0081-4
Heritability enrichment of specifically expressed genes identifies disease-relevant tissues and cell types
Abstract
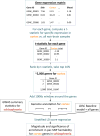
We introduce an approach to identify disease-relevant tissues and cell types by analyzing gene expression data together with genome-wide association study (GWAS) summary statistics. Our approach uses stratified linkage disequilibrium (LD) score regression to test whether disease heritability is enriched in regions surrounding genes with the highest specific expression in a given tissue. We applied our approach to gene expression data from several sources together with GWAS summary statistics for 48 diseases and traits (average N = 169,331) and found significant tissue-specific enrichments (false discovery rate (FDR) < 5%) for 34 traits. In our analysis of multiple tissues, we detected a broad range of enrichments that recapitulated known biology. In our brain-specific analysis, significant enrichments included an enrichment of inhibitory over excitatory neurons for bipolar disorder, and excitatory over inhibitory neurons for schizophrenia and body mass index. Our results demonstrate that our polygenic approach is a powerful way to leverage gene expression data for interpreting GWAS signals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




Comment in
-
Linking tissues to disease.Nat Rev Genet. 2018 Jun;19(6):328. doi: 10.1038/s41576-018-0009-y. Nat Rev Genet. 2018. PMID: 29686399 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 MH094714/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH103877/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH103346/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH103340/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH103339/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR063759/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH105881/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA194393/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH109978/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH106934/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA194393/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH103365/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG002295/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007753/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH103392/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MC_UU_12015/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH105472/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG009379/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UH2 AR067677/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH102791/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH107649/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH105898/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

