Transcriptome-wide association study of schizophrenia and chromatin activity yields mechanistic disease insights
- PMID: 29632383
- PMCID: PMC5942893
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-018-0092-1
Transcriptome-wide association study of schizophrenia and chromatin activity yields mechanistic disease insights
Abstract
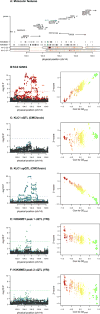
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified over 100 risk loci for schizophrenia, but the causal mechanisms remain largely unknown. We performed a transcriptome-wide association study (TWAS) integrating a schizophrenia GWAS of 79,845 individuals from the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium with expression data from brain, blood, and adipose tissues across 3,693 primarily control individuals. We identified 157 TWAS-significant genes, of which 35 did not overlap a known GWAS locus. Of these 157 genes, 42 were associated with specific chromatin features measured in independent samples, thus highlighting potential regulatory targets for follow-up. Suppression of one identified susceptibility gene, mapk3, in zebrafish showed a significant effect on neurodevelopmental phenotypes. Expression and splicing from the brain captured most of the TWAS effect across all genes. This large-scale connection of associations to target genes, tissues, and regulatory features is an essential step in moving toward a mechanistic understanding of GWAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 MH094268/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH094714/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F32 GM106584/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH057881/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH103877/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH103365/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH075916/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R00 MH113823/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH110927/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH103346/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH105472/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MR/P005748/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 MH103340/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH084053/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH105881/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD018164/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH080405/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH109528/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH085542/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH106934/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007753/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH103392/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH103339/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH097276/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG002219/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH093725/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005138/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM105857/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG009379/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 MH113823/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG009120/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH102791/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH107649/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH105898/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH066392/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MR/L010305/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH109978/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

