Dissecting the molecular pathophysiology of drug-induced liver injury
- PMID: 29632419
- PMCID: PMC5889818
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i13.1373
Dissecting the molecular pathophysiology of drug-induced liver injury
Abstract
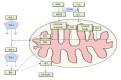
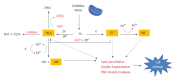
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) has become a major topic in the field of Hepatology and Gastroenterology. DILI can be clinically divided into three phenotypes: hepatocytic, cholestatic and mixed. Although the clinical manifestations of DILI are variable and the pathogenesis complicated, recent insights using improved preclinical models, have allowed a better understanding of the mechanisms that trigger liver damage. In this review, we will discuss the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying DILI. The toxicity of the drug eventually induces hepatocellular damage through multiple molecular pathways, including direct hepatic toxicity and innate and adaptive immune responses. Drugs or their metabolites, such as the common analgesic, acetaminophen, can cause direct hepatic toxicity through accumulation of reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial dysfunction. The innate and adaptive immune responses play also a very important role in the occurrence of idiosyncratic DILI. Furthermore, we examine common forms of hepatocyte death and their association with the activation of specific signaling pathways.
Keywords: Acetaminophen; Cell death; Drug-induced liver injury; Reactive oxygen species; Signaling pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Yu YC, Mao YM, Chen CW, Chen JJ, Chen J, Cong WM, Ding Y, Duan ZP, Fu QC, Guo XY, Hu P, Hu XQ, Jia JD, Lai RT, Li DL, Liu YX, Lu LG, Ma SW, Ma X, Nan YM, Ren H, Shen T, Wang H, Wang JY, Wang TL, Wang XJ, Wei L, Xie Q, Xie W, Yang CQ, Yang DL, Yu YY, Zeng MD, Zhang L, Zhao XY, Zhuang H; Drug-induced Liver Injury (DILI) Study Group; Chinese Society of Hepatology (CSH); Chinese Medical Association (CMA) CSH guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of drug-induced liver injury. Hepatol Int. 2017;11:221–241. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Miguel A, Azevedo LF, Araújo M, Pereira AC. Frequency of adverse drug reactions in hospitalized patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2012;21:1139–1154. - PubMed
-
- Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ. Sleisenger and Fordtran‘s Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. In: Chitturi S TN, Farrell GC, editor Hepatic drug metabolism and liver disease caused by drugs. Philadelphia; 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

