Biodegradable Polymeric Materials in Degradable Electronic Devices
- PMID: 29632879
- PMCID: PMC5879474
- DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.7b00595
Biodegradable Polymeric Materials in Degradable Electronic Devices
Abstract
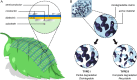
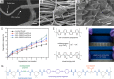
Biodegradable electronics have great potential to reduce the environmental footprint of devices and enable advanced health monitoring and therapeutic technologies. Complex biodegradable electronics require biodegradable substrates, insulators, conductors, and semiconductors, all of which comprise the fundamental building blocks of devices. This review will survey recent trends in the strategies used to fabricate biodegradable forms of each of these components. Polymers that can disintegrate without full chemical breakdown (type I), as well as those that can be recycled into monomeric and oligomeric building blocks (type II), will be discussed. Type I degradation is typically achieved with engineering and material science based strategies, whereas type II degradation often requires deliberate synthetic approaches. Notably, unconventional degradable linkages capable of maintaining long-range conjugation have been relatively unexplored, yet may enable fully biodegradable conductors and semiconductors with uncompromised electrical properties. While substantial progress has been made in developing degradable device components, the electrical and mechanical properties of these materials must be improved before fully degradable complex electronics can be realized.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




References
-
- Nair L. S.; Laurencin C. T. Biodegradable polymers as biomaterials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 762–798. 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2007.05.017. - DOI
-
- Amass W.; Amass A.; Tighe B. A review of biodegradable polymers: uses, current developments in the synthesis and characterization of biodegradable polyesters, blends of biodegradable polymers and recent advances in biodegradation studies. Polym. Int. 1998, 47, 89–144. 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0126(1998100)47:2<89::AID-PI86>3.0.CO;2-F. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

