US Army Soldiers With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 29633858
- PMCID: PMC6134313
- DOI: 10.1177/1932296818767700
US Army Soldiers With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
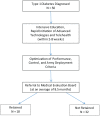
US Army soldiers diagnosed with type 1 diabetes were previously considered unfit for duty. For highly motivated soldiers, current advanced technologies allow the possibility of not only retention on active duty, but military deployment. We present our experience at Fort Bragg, North Carolina, taking care of soldiers newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Through intensive diabetes education, extensive military and physical training, optimization of diabetes technology, and remote real-time monitoring, soldiers are able to continue to serve their country in the most specialized roles.
Keywords: army; continuous glucose sensor; deployment; military; real-time; remote; self-monitoring of blood glucose; soldier; telemedicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Army Regulation 40-501. Standards of Medical Fitness. Washington, DC: Headquarters Department of the Army; 2017.
-
- Sawka MH, Burke LM, Eicher ER, Maughan RJ, Montain SJ, Stachenfeld NS. American College of Sports Medicine position stand. Exercise and fluid replacement. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007;39:377-390. - PubMed
-
- Thomas DT, Erdman KA, Burke LM. American College of Sports Medicine joint position statement. Nutrition and athletic performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2016;48:543-568. - PubMed
-
- Yardley JE, Colberg SR. Update on management of type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes in athletes. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2017;16:38-44. - PubMed
-
- Gregg EW, Zhuo X, Cheng YJ, Albright AL, Narayan KM, Thompson TJ. Trends in lifetime risk and years of life lost due to diabetes in the USA, 1985-2011: a modeling study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014;2:867-874. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical