Children with severe acute asthma admitted to Dutch PICUs: A changing landscape
- PMID: 29635844
- PMCID: PMC6032863
- DOI: 10.1002/ppul.24009
Children with severe acute asthma admitted to Dutch PICUs: A changing landscape
Abstract
The number of children requiring pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) admission for severe acute asthma (SAA) around the world has increased.
Objectives: We investigated whether this trend in SAA PICU admissions is present in the Netherlands.
Methods: A multicenter retrospective cohort study across all tertiary care PICUs in the Netherlands. Inclusion criteria were children (2-18 years) hospitalized for SAA between 2003 and 2013. Data included demographic data, asthma diagnosis, treatment, and mortality.
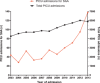
Results: In the 11-year study period 590 children (660 admissions) were admitted to a PICU with a threefold increase in the number of admissions per year over time. The severity of SAA seemed unchanged, based on the first blood gas, length of stay and mortality rate (0.6%). More children received highflow nasal cannula (P < 0.001) and fewer children needed invasive ventilation (P < 0.001). In 58% of the patients the maximal intravenous (IV) salbutamol infusion rate during PICU admission was 1 mcg/kg/min. However, the number of patients treated with IV salbutamol in the referring hospitals increased significantly over time (P = 0.005). The proportion of steroid-naïve patients increased from 35% to 54% (P = 0.004), with a significant increase in both age groups (2-4 years [P = 0.026] and 5-17 years [P = 0.036]).
Conclusions: The number of children requiring PICU admission for SAA in the Netherlands has increased. We speculate that this threefold increase is explained by an increasing number of steroid-naïve children, in conjunction with a lowered threshold for PICU admission, possibly caused by earlier use of salbutamol IV in the referring hospitals.
Keywords: intensive care; pediatric asthma; severe acute asthma; status asthmaticus; steroid-naïve.
© 2018 The Authors. Pediatric Pulmonology Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Lai RB CKW, Crane J, Foliaki S, Shah J, Weiland S. Global variation in the prevalence and severity of asthma symptoms: phase three of the International Study of Asthma and Allergies in Childhood (ISAAC). BMJ Open. 2009; 64:476–483. - PubMed
-
- Wijga AH, van Buul LW, Blokstra A, Wolse APH. Astma bij kinderen tot 12 jaar: resultaten van het PIAMA‐onderzoek. RIVM. 2011; 2011:25–28.
-
- Kaza V, Bandi V, Guntupalli KK. Acute severe asthma: recent advances. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2007; 13:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Nederlandse Vereniging voor Kindergeneeskunde, (NVK), (https://www.nvk/0/richtlijnen/acuutastma/acuutastma.pdf).
-
- van den Bosch GE, Merkus PJ, Buysse CM, et al. Risk factors for pediatric intensive care admission in children with acute asthma. Respir Care. 2012; 57:1391–1397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical