Prevalence of fecal viruses and bacteriophage in Canadian farmed mink (Neovison vison)
- PMID: 29635866
- PMCID: PMC6341152
- DOI: 10.1002/mbo3.622
Prevalence of fecal viruses and bacteriophage in Canadian farmed mink (Neovison vison)
Abstract
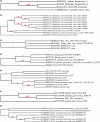
Recent viral metagenomic studies have demonstrated the diversity of eukaryotic viruses and bacteriophage shed in the feces of domestic species. Although enteric disease is a major concern in the commercial mink farming industry, few etiologic agents have been well characterized. This study aimed to identify viruses shed in the fecal matter of clinically healthy commercial mink from 40 southern Ontario farms. Viral RNA was extracted from 67 pooled fecal samples (30 adult female mink and 37 kit) and amplified for Illumina sequencing on the NextSeq platform, and the resulting contigs were trimmed and assembled using Trimmomatic 0.36.0 and Spades 3.8.0 in iVirus (CyVerse, AZ, USA) and SeqMan NGen 12 (DNAStar, WI, USA). Identification of assembled sequences >100 bp (Geneious 10.1.3) showed an abundance of bacteriophage sequences, mainly from families Siphoviridae (53%), Podoviridae (22%), Myoviridae (20%), Inoviridae (1%), Leviviridae (0.04%), Tectiviridae (0.01%), and Microviridae (0.01%). A diverse range of vertebrate viruses were detected, of which posavirus 3, mink bocavirus, gyroviruses, and avian-associated viruses were most abundant. Additionally, sequences from nonvertebrate viruses with water and soil-associated amebal and algal hosts were also highly prevalent. The results of this study show that viruses shed in the fecal matter of healthy commercial mink are highly diverse and could be closely associated with diet, and that more research is necessary to determine how the detected viruses may impact mink health.
Keywords: antimicrobial resistance; bacteriophage; fecal virome; mink.
© 2018 The Authors. MicrobiologyOpen published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Arnold, E. , Collier, L. , Balows, A. , & Sussman, M. (1997). Topley and Wilson's microbiology and microbial infections (9th ed.). New York, NY: John Wiley and Sons Inc..
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

