Circadian Misalignment and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Incidence in the United States
- PMID: 29636342
- PMCID: PMC6035064
- DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-17-1052
Circadian Misalignment and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Incidence in the United States
Abstract
Background: Circadian misalignment may increase the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The aim of this study was to examine the association between distance from time zone meridian, a proxy for circadian misalignment, and HCC risk in the United States adjusting for known HCC risk factors.Methods: Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) provided information on 56,347 HCC cases diagnosed between 2000 and 2014 from 16 population-based cancer registries in the United States. Distance from time zone meridian was estimated using the location of each SEER county's Center of Population in a geographic information system. Poisson regression with robust variance estimation was used to calculate incidence rate ratios (IRRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for the association between distance from time zone meridian and HCC risk adjusting for individual-level age at diagnosis, sex, race/ethnicity, year of diagnosis, SEER registry, and county-level prevalence of health conditions, lifestyle factors, shift work occupation, socioeconomic status, and demographic and environmental factors.Results: A 5-degree increase in longitude moving east to west within a time zone was associated with a statistically significant increased risk for HCC (IRR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.01-1.14, P = 0.03). A statistically significant positive association was observed among those <65 years old, while no association was observed among individuals ≥65 years old (Pfor interaction < 0.01).Conclusions: Circadian misalignment from residing in the western region of a time zone may impact hepatocarcinogenesis.Impact: Circadian misalignment may be an independent risk factor for HCC. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev; 27(7); 719-27. ©2018 AACR.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
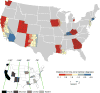
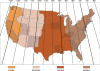
References
-
- Berson DM, Dunn FA, Takao M. Phototransduction by retinal ganglion cells that set the circadian clock. Science. 2002;295(5557):1070–3. - PubMed
-
- Czeisler CA, Allan JS, Strogatz SH, Ronda JM, Sanchez R, Rios CD, et al. Bright light resets the human circadian pacemaker independent of the timing of the sleep-wake cycle. Science. 1986;233:667–72. - PubMed
-
- Yang WS, Deng Q, Fan WY, Wang WY, Wang X. Light exposure at night, sleep duration, melatonin, and breast cancer: a dose-response analysis of observational studies. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2014;23(4):269–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

