Nanomedicine applications in women's health: state of the art
- PMID: 29636611
- PMCID: PMC5880180
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S97572
Nanomedicine applications in women's health: state of the art
Abstract
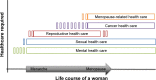
State-of-the-art applications of nanomedicine have the potential to revolutionize the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of a range of conditions and diseases affecting women's health. In this review, we provide a synopsis of potential applications of nanomedicine in some of the most dominant fields of women's health: mental health, sexual health, reproductive medicine, oncology, menopause-related conditions and dementia. We explore published studies arising from in vitro and in vivo experiments, and clinical trials where available, to reveal novel and highly promising therapeutic applications of nanomedicine in these fields. For the first time, we summarize the growing body of evidence relating to the use of nanomaterials as experimental tools for the detection, prevention, and treatment of significant diseases and conditions across the life course of a cisgender woman, from puberty to menopause; revealing the far-reaching and desirable theoretical impact of nanomedicine across different medical disciplines. We also present an overview of potential concerns regarding the therapeutic applications of nanomedicine and the factors currently restricting the growth of applied nanomedicine.
Keywords: dementia; menopause; mental health; nanomedicine; oncology; reproductive medicine; sexual health.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure EA is funded by the “National Teaching Assistant Program” of United Arab Emirates University. The other authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rethinking the application of nanoparticles in women's reproductive health and assisted reproduction.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2024;19(14):1231-1251. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2023-0346. Epub 2024 May 21. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38686941 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering nanosystems for regulating reproductive health in women.Theranostics. 2025 Jan 1;15(2):439-459. doi: 10.7150/thno.102626. eCollection 2025. Theranostics. 2025. PMID: 39744682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Women's health from a woman's point of view: a review of the literature.Health Care Women Int. 1986;7(3):255-75. doi: 10.1080/07399338609515739. Health Care Women Int. 1986. PMID: 3522518 Review.
-
Nanomedicine for Women's Health.Small. 2024 Oct;20(41):e2405178. doi: 10.1002/smll.202405178. Epub 2024 Jul 20. Small. 2024. PMID: 39032120 No abstract available.
-
Women's Reproductive Milestones and Cardiovascular Disease Risk: A Review of Reports and Opportunities From the CARDIA Study.J Am Heart Assoc. 2023 Mar 7;12(5):e028132. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.122.028132. Epub 2023 Feb 27. J Am Heart Assoc. 2023. PMID: 36847077 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Optimized nonionic emulsifier for the efficient delivery of astaxanthin nanodispersions to retina: in vivo and ex vivo evaluations.Drug Deliv. 2019 Dec;26(1):1222-1234. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2019.1682718. Drug Deliv. 2019. PMID: 31747793 Free PMC article.
-
De novo design of a nanoregulator for the dynamic restoration of ovarian tissue in cryopreservation and transplantation.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Jun 11;22(1):330. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02602-5. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 38862987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New hope for preventing preterm birth: The promise of vaginal nanoformulations.Placenta Reprod Med. 2022;1:107. Epub 2022 Jul 6. Placenta Reprod Med. 2022. PMID: 36425736 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Advanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Techniques: Technical Principles and Applications in Nanomedicine.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 23;14(7):1626. doi: 10.3390/cancers14071626. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35406399 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Situ Photo Responsive Biodegradable Nanoparticle Forming Intrauterine Implant for Drug Delivery to Treat Ovarian Diseases: A Rationale-based Review.Curr Radiopharm. 2024;17(4):313-319. doi: 10.2174/0118744710258313231105072931. Curr Radiopharm. 2024. PMID: 38031270 Review.
References
-
- Koopmans RJ, Aggeli A. Nanobiotechnology – quo vadis? Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010;13(3):327–334. - PubMed
-
- Emerich DF. Nanomedicine – prospective therapeutic and diagnostic applications. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2005;5(1):1–5. - PubMed
-
- Albanese A, Tang PS, Chan WCW. In: The effect of nanoparticle size, shape, and surface chemistry on biological systems. Yarmush ML, editor. Vol. 14. Palo Alto, CA: Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering; 2012. pp. 1–16. - PubMed
-
- High Quality Women’s Health Care: a proposal for change [webpage on the Internet] London: Royal College of Obstetrics and Gynaecologists; 2011. [Accessed February 20, 2017]. Available from: http://www.rcog.org.uk/high-quality-womens-health-care.
-
- Tomorrow’s Specialist RCOG [webpage on the Internet] London: Royal College of Obstetrics and Gynaecologists; 2011. [Accessed February 20, 2017]. Available from: https://www.rcog.org.uk/en/guidelines-research-services/guidelines/tomor....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

