miR-206 regulates 5-FU resistance by targeting Bcl-2 in colon cancer cells
- PMID: 29636622
- PMCID: PMC5881530
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S159093
miR-206 regulates 5-FU resistance by targeting Bcl-2 in colon cancer cells
Abstract
Introduction: Previous studies have found that miRNAs play a key role in drug resistance. Multiple reports show that miRNAs act as regulators in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells, but the role of miR-206 in CRC is still not well understood. The current study aimed to explore the potential function of miR-206 in 5-FU resistance.
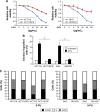
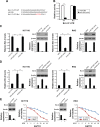
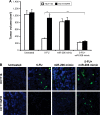
Methods: To indentify the role of miR-206 in 5-FU resistance, the expression of miR-206 was examined by real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) in 5-FU-resistant (FR) CRC (HCT116/FR and RKO/FR) and their parental cell lines. miR-206 mimic was transfected to 5-FU-FR CRC, and the 5-FU sensitivity was detected by MTS and flow cytometry. Using miRNA target prediction software, we found that miR-206 could target the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) sequence of Bcl-2.
Results: miR-206 was found to be downregulated in 5-FU-FR CRC in comparison with their parental cell lines, suggesting its crucial relevance for colon cancer biology. Downregulation of miR-206 promoted drug resistance and decreased apoptosis of parental cells, while overexpression of miR-206 promoted drug cytotoxicity and apoptosis of HCT116/FR cells. We also identified miR-206 targeting Bcl-2 directly in CRC, which is required for miR-206 mediated-5-FU resistance.
Conclusion: Our results show that miR-206 targets Bcl-2 to mediate chemoresistance, proliferation, and apoptosis in CRC. This study provides a novel promising candidate for colon cancer therapy.
Keywords: 5-FU; Bcl-2; colorectal cancer; miR-206; resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
GDPD5, a target of miR-195-5p, is associated with metastasis and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 May;101:945-952. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.028. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29635904
-
miR-106a Reduces 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) Sensitivity of Colorectal Cancer by Targeting Dual-Specificity Phosphatases 2 (DUSP2).Med Sci Monit. 2018 Jul 16;24:4944-4951. doi: 10.12659/MSM.910016. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 30011263 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-149 Increases the Sensitivity of Colorectal Cancer Cells to 5-Fluorouracil by Targeting Forkhead Box Transcription Factor FOXM1.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;39(2):617-29. doi: 10.1159/000445653. Epub 2016 Jul 15. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27415661
-
MicroRNA-218 is a prognostic indicator in colorectal cancer and enhances 5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis by targeting BIRC5.Carcinogenesis. 2015 Dec;36(12):1484-93. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv145. Epub 2015 Oct 6. Carcinogenesis. 2015. PMID: 26442524
-
Upregulation of microRNA-135b and microRNA-182 promotes chemoresistance of colorectal cancer by targeting ST6GALNAC2 via PI3K/AKT pathway.Mol Carcinog. 2017 Dec;56(12):2669-2680. doi: 10.1002/mc.22710. Epub 2017 Aug 21. Mol Carcinog. 2017. PMID: 28767179
Cited by
-
Recent advances in the diagnostic and therapeutic roles of microRNAs in colorectal cancer progression and metastasis.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 13;12:911856. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.911856. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36313731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circ-PRKDC Contributes to 5-Fluorouracil Resistance of Colorectal Cancer Cells by Regulating miR-375/FOXM1 Axis and Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Jun 23;13:5939-5953. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S253468. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32606803 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin Reduces Colorectal Cancer Cell Proliferation and Migration and Slows In Vivo Growth of Liver Metastases in Rats.Biomedicines. 2021 Sep 8;9(9):1183. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9091183. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34572369 Free PMC article.
-
CircTM7SF3 contributes to oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis, inflammation and oxidative stress through targeting miR-206/ASPH axis in atherosclerosis cell model in vitro.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021 Feb 2;21(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12872-020-01800-x. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021. PMID: 33526034 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 22 promotes proliferation and metastasis in human colon cancer.Oncol Lett. 2019 Nov;18(5):5567-5576. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10872. Epub 2019 Sep 16. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31612065 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Kuilenburg AB, Maring JG. Evaluation of 5-fluorouracil pharmacokinetic models and therapeutic drug monitoring in cancer patients. Pharmacogenomics. 2013;14:799–811. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

