Altered Gray Matter Volume and Resting-State Connectivity in Individuals With Internet Gaming Disorder: A Voxel-Based Morphometry and Resting-State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study
- PMID: 29636704
- PMCID: PMC5881242
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00077
Altered Gray Matter Volume and Resting-State Connectivity in Individuals With Internet Gaming Disorder: A Voxel-Based Morphometry and Resting-State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study
Abstract
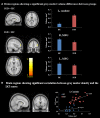
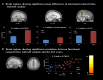
Neuroimaging studies on the characteristics of individuals with Internet gaming disorder (IGD) have been accumulating due to growing concerns regarding the psychological and social problems associated with Internet use. However, relatively little is known about the brain characteristics underlying IGD, such as the associated functional connectivity and structure. The aim of this study was to investigate alterations in gray matter (GM) volume and functional connectivity during resting state in individuals with IGD using voxel-based morphometry and a resting-state connectivity analysis. The participants included 20 individuals with IGD and 20 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. Resting-state functional and structural images were acquired for all participants using 3 T magnetic resonance imaging. We also measured the severity of IGD and impulsivity using psychological scales. The results show that IGD severity was positively correlated with GM volume in the left caudate (p < 0.05, corrected for multiple comparisons), and negatively associated with functional connectivity between the left caudate and the right middle frontal gyrus (p < 0.05, corrected for multiple comparisons). This study demonstrates that IGD is associated with neuroanatomical changes in the right middle frontal cortex and the left caudate. These are important brain regions for reward and cognitive control processes, and structural and functional abnormalities in these regions have been reported for other addictions, such as substance abuse and pathological gambling. The findings suggest that structural deficits and resting-state functional impairments in the frontostriatal network may be associated with IGD and provide new insights into the underlying neural mechanisms of IGD.
Keywords: Internet gaming disorder; caudate nucleus; functional connectivity; middle frontal gyrus; resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging; voxel-based morphometry.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Abnormal Granger causal connectivity based on altered gray matter volume and associated neurotransmitters of adolescents with internet gaming disorder revealed by a multimodal neuroimaging study.Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2024 Dec;70:101472. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2024.101472. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39486388 Free PMC article.
-
Frontostriatal circuits, resting state functional connectivity and cognitive control in internet gaming disorder.Addict Biol. 2017 May;22(3):813-822. doi: 10.1111/adb.12348. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Addict Biol. 2017. PMID: 26769234
-
Abnormal prefrontal cortex resting state functional connectivity and severity of internet gaming disorder.Brain Imaging Behav. 2016 Sep;10(3):719-29. doi: 10.1007/s11682-015-9439-8. Brain Imaging Behav. 2016. PMID: 26311395
-
Meta-analysis of structural and functional brain alterations in internet gaming disorder.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Oct 25;13:1029344. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1029344. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 37033880 Free PMC article.
-
Large-scale network dysfunction in youths with Internet gaming disorder: a meta-analysis of resting-state functional connectivity studies.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2021 Jul 13;109:110242. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2021.110242. Epub 2021 Jan 9. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33434637 Review.
Cited by
-
Higher levels of (Internet) Gaming Disorder symptoms according to the WHO and APA frameworks associate with lower striatal volume.J Behav Addict. 2020 Oct 2;9(3):598-605. doi: 10.1556/2006.2020.00066. Print 2020 Oct 12. J Behav Addict. 2020. PMID: 33010145 Free PMC article.
-
Neurobiological mechanisms underlying internet gaming disorder .Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2020 Jun;22(2):113-126. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2020.22.2/aweinstein. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32699511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of frontostriatal circuits in adolescent nicotine addiction and internet gaming disorder.J Behav Addict. 2022 Jan 19;11(1):26-39. doi: 10.1556/2006.2021.00086. Print 2022 Mar 28. J Behav Addict. 2022. PMID: 35049521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gaming disorder: Neural mechanisms and ongoing debates.J Behav Addict. 2025 Jan 8;14(1):55-78. doi: 10.1556/2006.2024.00071. Print 2025 Mar 28. J Behav Addict. 2025. PMID: 39786382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shared gray matter alterations in individuals with diverse behavioral addictions: A voxel-wise meta-analysis.J Behav Addict. 2020 Apr 1;9(1):44-57. doi: 10.1556/2006.2020.00006. J Behav Addict. 2020. PMID: 32359230 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. Washington, DC: APA; (2013).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

