MicroRNA-337 regulates the PI3K/AKT and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways to inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma progression by targeting high-mobility group AT-hook 2
- PMID: 29636997
- PMCID: PMC5883092
MicroRNA-337 regulates the PI3K/AKT and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways to inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma progression by targeting high-mobility group AT-hook 2
Abstract
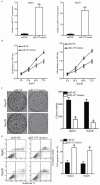
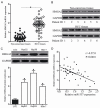
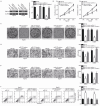
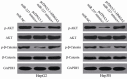
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) serve as major regulators during the tumorigenesis and tumor development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In addition, miRNAs may serve as new promising biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis and as effective therapeutic targets for patients with this malignancy. Therefore, understanding the association between miRNAs and HCC may be beneficial to discover novel therapeutic approaches towards diagnosis and treatments. Results of this study showed that miRNA-337 (miR-337) was markedly downregulated in HCC tissues and cell lines. Decreased miR-337 expression was significantly associated with the TNM stage and lymph node metastasis of HCC. Ectopic expression of miR-337 prohibited the proliferation, colony formation, migration, and invasion of HCC cells. It also promoted the apoptosis in vitro and reduced the tumor growth in vivo of these cells. High-mobility group AT-hook 2 (HMGA2) was identified as a direct target gene of miR-337 in HCC through a series of experiments. HMGA2 was significantly overexpressed in HCC tissues and negatively correlated with miR-337 expression. Moreover, the functions of HMGA2 inhibition were similar to those induced by miR-337 in HCC. Restored HMGA2 expression rescued the tumor-suppressive roles of miR-337 overexpression in HCC. Furthermore, miR-337 overexpression inhibited the activation of PI3K/AKT and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways in HCC both in vitro and in vivo. This study demonstrated that miR-337 may play tumor-suppressing roles in HCC, at least partly, via directly targeting HMGA2 and inhibiting the PI3K/AKT and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways. Therefore, miR-337 may be a novel and effective target for the therapeutic treatment of patients with HCC.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; high-mobility group AT-hook 2; microRNA-337; tumor suppressor.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures




Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-504 functions as a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma through inhibiting Frizzled-7-mediated-Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Nov;107:754-762. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.150. Epub 2018 Aug 21. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 30142536
-
Methylation-mediated repression of microRNA-129-2 suppresses cell aggressiveness by inhibiting high mobility group box 1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 14;7(24):36909-36923. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9377. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27191994 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-194 inhibits cell invasion and migration in hepatocellular carcinoma through PRC1-mediated inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Dig Liver Dis. 2019 Sep;51(9):1314-1322. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2019.02.012. Epub 2019 Mar 1. Dig Liver Dis. 2019. PMID: 30948333
-
Interplay of Wnt β-catenin pathway and miRNAs in HBV pathogenesis leading to HCC.Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2019 Aug;43(4):373-386. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2018.09.012. Epub 2018 Oct 28. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30377095 Review.
-
The Key Role of microRNAs in Initiation and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 18;12:950374. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.950374. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35924150 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High Mobility Group A (HMGA): Chromatin Nodes Controlled by a Knotty miRNA Network.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 22;21(3):717. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030717. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31979076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of MicroRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Cancer. 2018 Sep 8;9(19):3557-3569. doi: 10.7150/jca.26350. eCollection 2018. J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30310513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay of miRNAs and Canonical Wnt Signaling Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Jun 21;9:657. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00657. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29977206 Free PMC article.
-
Fetal Brain-Derived Exosomal miRNAs from Maternal Blood: Potential Diagnostic Biomarkers for Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders (FASDs).Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 27;25(11):5826. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115826. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892014 Free PMC article.
-
EZH2-mediated epigenetic silencing of tumor-suppressive let-7c/miR-99a cluster by hepatitis B virus X antigen enhances hepatocellular carcinoma progression and metastasis.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Sep 9;23(1):199. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-03002-9. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 37689710 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012;379:1245–1255. - PubMed
-
- Vertemati M, Moscheni C, Petrella D, Lamperti L, Cossa M, Gambacorta M, Goffredi M, Vizzotto L. Morphometric analysis of hepatocellular nodular lesions in HCV cirrhosis. Pathol Res Pract. 2012;208:240–244. - PubMed
-
- Liang T, Chen EQ, Tang H. Hepatitis B virus gene mutations and hepatocarcinogenesis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14:4509–4513. - PubMed
-
- Gao J, Xie L, Yang WS, Zhang W, Gao S, Wang J, Xiang YB. Risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma--current status and perspectives. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2012;13:743–752. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
