Reactive oxygen species generation mediated by NADPH oxidase and PI3K/Akt pathways contribute to invasion of Streptococcus agalactiae in human endothelial cells
- PMID: 29641644
- PMCID: PMC5887998
- DOI: 10.1590/0074-02760170421
Reactive oxygen species generation mediated by NADPH oxidase and PI3K/Akt pathways contribute to invasion of Streptococcus agalactiae in human endothelial cells
Abstract
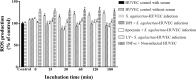
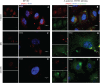
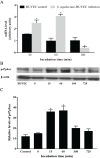
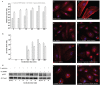
BACKGROUND Streptococcus agalactiae can causes sepsis, pneumonia, and meningitis in neonates, the elderly, and immunocompromised patients. Although the virulence properties of S. agalactiae have been partially elucidated, the molecular mechanisms related to reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation in infected human endothelial cells need further investigation. OBJECTIVES This study aimed to evaluate the influence of oxidative stress in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) during S. agalactiae infection. METHODS ROS production during S. agalactiae-HUVEC infection was detected using the probe CM-H2DCFDA. Microfilaments labelled with phalloidin-FITC and p47phox-Alexa 546 conjugated were analysed by immunofluorescence. mRNA levels of p47phox (NADPH oxidase subunit) were assessed using Real Time qRT-PCR. The adherence and intracellular viability of S. agalactiae in HUVECs with or without pre-treatment of DPI, apocynin (NADPH oxidase inhibitors), and LY294002 (PI3K inhibitor) were evaluated by penicillin/gentamicin exclusion. Phosphorylation of p47phox and Akt activation by S. agalactiae were evaluated by immunoblotting analysis. FINDINGS Data showed increased ROS production 15 min after HUVEC infection. Real-Time qRT-PCR and western blotting performed in HUVEC infected with S. agalactiae detected alterations in mRNA levels and activation of p47phox. Pre-treatment of endothelial cells with NADPH oxidase (DPI and apocynin) and PI3K/Akt pathway (LY294002) inhibitors reduced ROS production, bacterial intracellular viability, and generation of actin stress fibres in HUVECs infected with S. agalactiae. CONCLUSIONS ROS generation via the NADPH oxidase pathway contributes to invasion of S. agalactiae in human endothelial cells accompanied by cytoskeletal reorganisation through the PI3K/Akt pathway, which provides novel evidence for the involvement of oxidative stress in S. agalactiae pathogenesis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Naringin inhibits TNF-α induced oxidative stress and inflammatory response in HUVECs via Nox4/NF-κ B and PI3K/Akt pathways.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014;15(12):1173-82. doi: 10.2174/1389201015666141111114442. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25391245
-
Aspirin prevents resistin-induced endothelial dysfunction by modulating AMPK, ROS, and Akt/eNOS signaling.J Vasc Surg. 2012 Apr;55(4):1104-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2011.10.011. Epub 2012 Jan 14. J Vasc Surg. 2012. PMID: 22244860
-
Cigarette smoke extract upregulates heme oxygenase-1 via PKC/NADPH oxidase/ROS/PDGFR/PI3K/Akt pathway in mouse brain endothelial cells.J Neuroinflammation. 2011 Aug 24;8:104. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-104. J Neuroinflammation. 2011. PMID: 21861928 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophils to the ROScue: Mechanisms of NADPH Oxidase Activation and Bacterial Resistance.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Aug 25;7:373. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00373. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28890882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of plant respiratory burst oxidase homologs in stress responses.Free Radic Res. 2018 Aug;52(8):826-839. doi: 10.1080/10715762.2018.1473572. Epub 2018 Jul 3. Free Radic Res. 2018. PMID: 29732902 Review.
Cited by
-
Kalanchoe brasiliensis Cambess., a Promising Natural Source of Antioxidant and Antibiotic Agents against Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens for the Treatment of Salmonella Gastroenteritis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Nov 11;2019:9245951. doi: 10.1155/2019/9245951. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31827708 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway or Overexpression of Beclin1 Blocks Reinfection of Streptococcus pneumoniae After Infection of Influenza A Virus in Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia.Inflammation. 2019 Oct;42(5):1741-1753. doi: 10.1007/s10753-019-01035-9. Inflammation. 2019. PMID: 31267272 Free PMC article.
-
Heat shock protein 90 inhibitor AUY922 attenuates platelet-derived growth factor-BB-induced migration and proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020 May 1;24(3):241-248. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2020.24.3.241. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32392915 Free PMC article.
-
Gestational Fisetin Exerts Neuroprotection by Regulating Mitochondria-Directed Canonical Wnt Signaling, BBB Integrity, and Apoptosis in Prenatal VPA-Induced Rodent Model of Autism.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Jul;61(7):4001-4020. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03826-6. Epub 2023 Dec 4. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38048031
-
Sputum Microbiota in Coal Workers Diagnosed with Pneumoconiosis as Revealed by 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing.Life (Basel). 2022 Jun 2;12(6):830. doi: 10.3390/life12060830. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35743861 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abid MR, Spokes KC, Shih SC, Aird WC. NADPH oxidase activity selectively modulates vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(48):35373–35385. - PubMed
-
- Barbuti G, Moschioni M, Fumarulo R, Censini S, Montemurro P. Streptococcus pneumoniae modulates the respiratory burst response in human neutrophils. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2010;60(1):57–62. - PubMed
-
- Bülbül N, Pala E, İğci YZ, Göğebakan B, Öztuzcu S, Cengiz B, et al. NADPH oxidase p22phox gene expression in ulcerative colitis. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2014;25(6):634–638. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

