A New Inflammatory Marker: Elevated Monocyte to HDL Cholesterol Ratio Associated with Smoking
- PMID: 29642607
- PMCID: PMC5920450
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm7040076
A New Inflammatory Marker: Elevated Monocyte to HDL Cholesterol Ratio Associated with Smoking
Abstract
Objectives: The adverse effects of smoking in various pathologies are mediated by its effects on the inflammatory system. The monocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) ratio (MHR) has recently emerged as an indicator of inflammation. We aimed to investigate the relationship between MHR and cigarette smoking.
Patients and methods: Three hundred and ninety seven consecutive participants who smoke and 515 healthy subjects with no history of smoking enrolled in the study. Complete blood count parameters and lipid profile were analyzed in all study participants. Smoking habits were calculated as pack.years and number of cigarettes smoked per day.
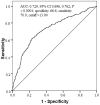
Results: MHR levels were significantly higher in smokers compared to non-smokers (respectively, 15.71 (12.02-20.00) and 11.17 (8.50-14.16), p < 0.0001)). Pearson's correlation analysis revealed a weak but positive correlation between pack.year and MHR in the smokers group, and there was a moderate positive correlation between the number of cigarettes smoked daily and MHR in the group. In receiver operating characteristics (ROC) analyses, it was determined that a MHR value >13.00 measured in smoker participants at application had a predictive specificity of 66.6% and sensitivity of 70.0% for smoking (area under the curve [AUC] 0.729, 95% CI 0.696, 0.762; p < 0.0001).
Conclusions: Elevated MHR is associated with cigarette smoking and may be a useful indicator of a systemic inflammatory response in smokers. Smoker participants who have high MHR levels can easily be identified during routine complete blood count (CBC) analysis and could possibly benefit from preventive treatment.
Keywords: inflammation; monocyte to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; smoking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organisation: Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic. Implementing Smoke-Free Environments. [(accessed on 25 December 2017)];2009 Available online: http://www.who.int/tobacco/mpower/2009/en.
-
- Collishaw N.E., Lopez A.D. Prevalence of cigarette smoking in developing countries. Tob. Control. 1995;4:327. doi: 10.1136/tc.4.4.327. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

