The Assessment of Clinical Usage and Prognostic Value of YKL-40 Serum Levels in Patients With Rectal Cancer Without Distant Metastasis
- PMID: 29642772
- PMCID: PMC5900806
- DOI: 10.1177/1533033818765209
The Assessment of Clinical Usage and Prognostic Value of YKL-40 Serum Levels in Patients With Rectal Cancer Without Distant Metastasis
Abstract
Background: Colorectal cancer is one of the most common and significant malignancies in the world. YKL-40 (chitinase-3-like protein 1) is involved in cell proliferation, migration, inflammation, and tissue remodeling; and serum levels of YKL-40 are associated with patient outcome in various cancers. The aim of this study was to assess the potential clinical usage of YKL-40 pretreatment serum levels as a prognostic biomarker in rectal cancer.
Methods: Concentrations of YKL-40 and standard tumor marker-Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)-were assessed in serum of 83 patients with rectal cancer without distant metastasis, and association with clinicopathological characteristics and disease-free and overall survival was evaluated.
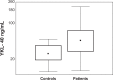
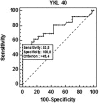
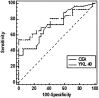
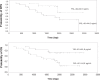
Results: Concentration of YKL-40 was significantly higher in serum of patients with rectal cancer compared to healthy controls ( P = .0001), and YKL-40 levels were able to predict rectal cancer (area under the Receiver Operating Characteristic [ROC] curve = .769) with higher accuracy than CEA (area under the ROC curve = .728) in patients with early stage disease. Increased YKL-40 levels were significantly associated with age ( P = .001); however, no association with other clinicopathological characteristics was observed. Finally, in patients with recurrence, the percentage of cases with increased concentration of YKL-40 was significantly higher than in patients without recurrence ( P = .041), and Kaplan-Meier analysis demonstrated that elevated YKL-40 concentration is a predictor of poor overall survival in patients with rectal cancer.
Conclusion: Pretreatment serum levels of YKL-40 may be a novel prognostic factor of overall and disease-free survival in patients with nonmetastatic colorectal cancer.
Keywords: YKL-40; biomarker; prognostic factor; rectal cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Preoperative serum levels of YKL 40 and CA125 as a prognostic indicators in patients with endometrial cancer.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2017 Aug;215:141-147. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2017.06.021. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2017. PMID: 28624692
-
Elevated pretreatment serum concentration of YKL-40: an independent prognostic biomarker for poor survival in patients with colorectal cancer.Med Oncol. 2014 Aug;31(8):85. doi: 10.1007/s12032-014-0085-6. Epub 2014 Jul 5. Med Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24996799
-
Evaluation of preoperative serum markers for individual patient prognosis in stage I-III rectal cancer.Tumour Biol. 2014 Oct;35(10):10237-48. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2338-6. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Tumour Biol. 2014. PMID: 25027407
-
The role of YKL-40 in a cancerous process.Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2016 Dec 27;70(0):1286-1299. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2016. PMID: 28026831 Review.
-
Serum YKL-40, a new prognostic biomarker in cancer patients?Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2006 Feb;15(2):194-202. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-05-0011. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2006. PMID: 16492905 Review.
Cited by
-
The Prognostic Value of Pre-Treatment Circulating Biomarkers of Systemic Inflammation (CRP, dNLR, YKL-40, and IL-6) in Vulnerable Older Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Receiving Palliative Chemotherapy-The Randomized NORDIC9-Study.J Clin Med. 2022 Sep 23;11(19):5603. doi: 10.3390/jcm11195603. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36233472 Free PMC article.
-
Do Elevated YKL-40 Levels Drive the Immunosuppressive Tumor Microenvironment in Colorectal Cancer? Assessment of the Association of the Expression of YKL-40, MMP-8, IL17A, and PD-L1 with Coexisting Type 2 Diabetes, Obesity, and Active Smoking.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Mar 27;45(4):2781-2797. doi: 10.3390/cimb45040182. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37185706 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Value of Serum Chitinase-3-Like Protein 1 for Liver Fibrosis: A Meta-analysis.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Mar 20;2022:3227957. doi: 10.1155/2022/3227957. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35360517 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Targeting via siRNA-COG3 to Suppress Tumor Progression in Mice and Inhibit Cancer Metastasis and Angiogenesis in Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines.Microrna. 2024;13(2):140-154. doi: 10.2174/0122115366275856240101083442. Microrna. 2024. PMID: 38243930
-
CHI3L1 promotes proliferation and improves sensitivity to cetuximab in colon cancer cells by down-regulating p53.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Jan;34(1):e23026. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23026. Epub 2019 Sep 19. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 31536166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(5):E359–E386. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, Desantis C, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64(2):104–117. - PubMed
-
- Fuksiewicz M, Kotowicz B, Rutkowski A, Kowalska M. The matrix metalloproteinase-7 and pro-enzyme of metalloproteinase-1 as a potential marker for patients with rectal cancer without distant metastasis. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(5):3629–3635. - PubMed
-
- Szczepanik AM, Siedlar M, Szura M, et al. Preoperative serum chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 levels and prognosis in colorectal cancer. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2015;125(6):443–451. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

