Exosomal miRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma development and clinical responses
- PMID: 29642941
- PMCID: PMC5896112
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-018-0579-3
Exosomal miRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma development and clinical responses
Abstract
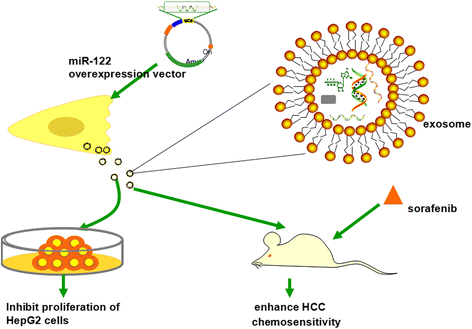
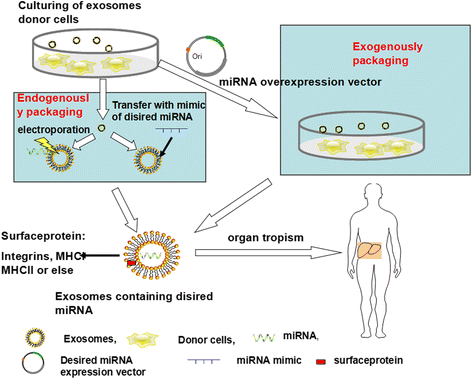
Hepatocellular carcinoma remains the sixth most lethal malignancy in the world. While HCC is often diagnosed via current biomarkers at a late stage, early detection of HCC has proven to be very difficult. Recent studies have focused on using exosomal miRNAs in clinical diagnostics and therapeutics, because they have improved stability in exosomes than as free miRNAs themselves. Exosomal miRNAs act through novel mechanisms for inducing cellular responses in a variety of biological circumstances. Dysregulated expression of miRNAs in exosomes can also accelerate HCC progression, including cell proliferation and metastasis, via alteration of a network of genes. Growing evidence demonstrates that exosomal miRNAs can affect many aspects of physiological and pathological conditions in HCC and indicates that miRNAs in exosomes can not only serve as sensitive biomarkers for cancer diagnostics and recurrence but can also potentially be used as therapeutics to target HCC progression. In this review, we summarize the latest findings between exosomal miRNAs and HCC, in order to better comprehend the functions and applications in HCC. Moreover, we discuss critical issues to consider when developing anti-tumor exosomal miRNAs as a novel therapeutic strategy for treating HCC in the clinic.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Exosome; Hepatocellular carcinoma; miRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

