[Correlation between expressions of VEGF and TRPC6 and their roles in podocyte injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy]
- PMID: 29643035
- PMCID: PMC6744170
- DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4254.2018.03.09
[Correlation between expressions of VEGF and TRPC6 and their roles in podocyte injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy]
Abstract
Objective: To analyze the correlation between the expressions of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and transient receptor potential canonical 6 (TRPC6) and their role in podocyte injury in rats with diabetic nephropathy.
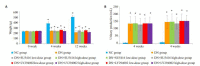
Methods: Forty SD rats with diabetic nephropathy induced by intraperitoneal injection of 65 mg/kg streptozotocin were randomized equally into 5 groups, including a diabetic nephropathy model group and 4 treatment groups, with 8 normal SD rats as the normal control group. In the 4 treatment groups, the rats received intraperitoneal injections with SU5416 at 5 mg/kg or 10 mg/kg twice a week or with LY294002 at 1 mg/kg or 2 mg/kg once daily for 8 weeks. Blood glucose, serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen, and 24-h urinary protein levels of the rats were detected at different time points, and the pathologies in the renal tissue were observed using HE staining, PAS staining and immunohistochemistry. The expressions of VEGF, nephrin, and TRPC6 at mRNA and protein levels were detected using RT-PCR and Western blotting.
Results: Compared with normal control rats, the diabetic rats showed significantly increased fasting blood glucose, serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen and 24-h urinary protein levels with decreased expressions of nephrin mRNA and protein (P<0.05) and increased expressions of VEGF and TRPC6 (P<0.05). Compared with the untreated diabetic rats, the rats with SU5416 treatment showed increased 24-h urinary protein, urea nitrogen, and nephrin expression and decreased TRPC6 expression without significant changes in fasting blood glucose, serum creatinine, or VEGF expression. The rats treated with LY294002 showed decreased 24-h urinary protein and TRPC6 expression without significant changes in fasting blood glucose, serum creatinine, urea nitrogen, or expressions of nephrin and VEGF.
Conclusion: The regulatory effect of VEGF on TRPC6 can be blocked by inhibiting VEGFR-2 or blocking PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
目的: 探讨血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)与瞬时受体电位阳离子通道蛋白6(TRPC6)有无相关性及其相互作用的可能机制。
方法: 随机取正常SD大鼠8只作为正常对照组,腹腔注射链脲佐菌素(STZ)65 mg/kg建立糖尿病肾病大鼠模型40只,并随机分为5组,每组8只。正常对照组及糖尿病肾病组不干预,其余4组分别给予SU5416 10 mg/kg、5 mg/kg(2次/周)以及LY294002 2 mg/kg、1 mg/kg(1次/d)腹腔注射干预8周。检测大鼠血肌酐、尿素氮及24 h尿蛋白生化指标变化情况,观察糖尿病肾病大鼠肾脏组织的病理改变,同时采用Realtime PCR及Western blot观察VEGF、Nephrin、TRPC6 mRNA表达及蛋白质的变化。
结果: 与正常对照组相比,糖尿病肾病组大鼠空腹血糖、血肌酐、尿素氮、24 h尿蛋白升高,Nephrin的表达下降,VEGF及TRPC6的表达升高(P < 0.05)。SU5416干预后24 h尿蛋白及尿素氮下降,Nephrin表达升高,VEGF表达无明显变化,TRPC6表达下降(P < 0.05)。LY294002干预后24 h尿蛋白下降,Nephrin及VEGF表达无明显变化,TRPC6表达下降(P < 0.05)。
结论: VEGF对TRPC6的调控作用可能是通过PI3K/Akt通路实现的。抑制VEGFR-2和/或者阻断PI3K/Akt信号通路可阻断VEGF对TRPC6的这种调控作用。
Figures








References
-
- Shankland SJ. The podocyte's response to injury: role in proteinuria and glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int. 2006;69(12):2131–47. doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5000410. [Shankland SJ. The podocyte's response to injury: role in proteinuria and glomerulosclerosis[J]. Kidney Int, 2006, 69(12): 2131-47.] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen S, Chen H, Liu Q, et al. Effect of simvastatin on the expression of nephrin, podocin, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in podocytes of diabetic rat. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(10):18225–34. [Chen S, Chen H, Liu Q, et al. Effect of simvastatin on the expression of nephrin, podocin, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in podocytes of diabetic rat[J]. Int J Clin Exp Med, 2015, 8 (10): 18225-34.] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Winn MP, Conlon PJ, Lynn KL, et al. A mutation in the TRPC6 cation channel causes familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Science. 2005;308(5729):1801–4. doi: 10.1126/science.1106215. [Winn MP, Conlon PJ, Lynn KL, et al. A mutation in the TRPC6 cation channel causes familial focal segmental glomerulosclerosis [J]. Science, 2005, 308(5729): 1801-4.] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Moeller CC, Wei CL, Altintas MM, et al. Induction of TRPC6 channel in acquired forms of proteinuric kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18(1):29–36. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2006091010. [Moeller CC, Wei CL, Altintas MM, et al. Induction of TRPC6 channel in acquired forms of proteinuric kidney disease[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2007, 18(1): 29-36.] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Schlondorff JS, Pollak MR. TRPC6 in glomerular health and disease: what we know and what we believe. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2006;17(6):667–74. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2006.11.003. [Schlondorff JS, Pollak MR. TRPC6 in glomerular health and disease: what we know and what we believe[J]. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2006, 17(6): 667-74.] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
