Widespread changes in transcriptome profile of human mesenchymal stem cells induced by two-dimensional nanosilicates
- PMID: 29643075
- PMCID: PMC5924886
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1716164115
Widespread changes in transcriptome profile of human mesenchymal stem cells induced by two-dimensional nanosilicates
Abstract
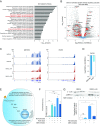
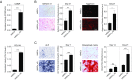
Two-dimensional nanomaterials, an ultrathin class of materials such as graphene, nanoclays, transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs), and transition metal oxides (TMOs), have emerged as a new generation of materials due to their unique properties relative to macroscale counterparts. However, little is known about the transcriptome dynamics following exposure to these nanomaterials. Here, we investigate the interactions of 2D nanosilicates, a layered clay, with human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) at the whole-transcriptome level by high-throughput sequencing (RNA-seq). Analysis of cell-nanosilicate interactions by monitoring changes in transcriptome profile uncovered key biophysical and biochemical cellular pathways triggered by nanosilicates. A widespread alteration of genes was observed due to nanosilicate exposure as more than 4,000 genes were differentially expressed. The change in mRNA expression levels revealed clathrin-mediated endocytosis of nanosilicates. Nanosilicate attachment to the cell membrane and subsequent cellular internalization activated stress-responsive pathways such as mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), which subsequently directed hMSC differentiation toward osteogenic and chondrogenic lineages. This study provides transcriptomic insight on the role of surface-mediated cellular signaling triggered by nanomaterials and enables development of nanomaterials-based therapeutics for regenerative medicine. This approach in understanding nanomaterial-cell interactions illustrates how change in transcriptomic profile can predict downstream effects following nanomaterial treatment.
Keywords: 2D nanomaterials; RNA-seq; human mesenchymal stem cells; nanosilicates; whole-transcriptome sequencing.
Copyright © 2018 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: J.K.C. and A.K.G. are coauthors on US Patent Application No. WO2017112802 A1 published on June 29, 2017 (US Provisional Patent Application No. 62/270,403 filed on December 21, 2015).
Figures


References
-
- Butler SZ, et al. Progress, challenges, and opportunities in two-dimensional materials beyond graphene. ACS Nano. 2013;7:2898–2926. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Tan C, Zhang H, Wang L. Two-dimensional graphene analogues for biomedical applications. Chem Soc Rev. 2015;44:2681–2701. - PubMed
-
- Chimene D, Alge DL, Gaharwar AK. Two-dimensional nanomaterials for biomedical applications: Emerging trends and future prospects. Adv Mater. 2015;27:7261–7284. - PubMed
-
- Jiang W, Kim BYS, Rutka JT, Chan WCW. Nanoparticle-mediated cellular response is size-dependent. Nat Nanotechnol. 2008;3:145–150. - PubMed
-
- Kerativitayanan P, Carrow JK, Gaharwar AK. Nanomaterials for engineering stem cell responses. Adv Healthc Mater. 2015;4:1600–1627. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

