Structural control of caspase-generated glutamyl-tRNA synthetase by appended noncatalytic WHEP domains
- PMID: 29643180
- PMCID: PMC5995526
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.807503
Structural control of caspase-generated glutamyl-tRNA synthetase by appended noncatalytic WHEP domains
Abstract
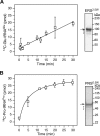
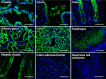
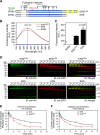
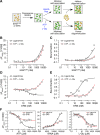
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases are ubiquitous, evolutionarily conserved enzymes catalyzing the conjugation of amino acids onto cognate tRNAs. During eukaryotic evolution, tRNA synthetases have been the targets of persistent structural modifications. These modifications can be additive, as in the evolutionary acquisition of noncatalytic domains, or subtractive, as in the generation of truncated variants through regulated mechanisms such as proteolytic processing, alternative splicing, or coding region polyadenylation. A unique variant is the human glutamyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetase (EPRS) consisting of two fused synthetases joined by a linker containing three copies of the WHEP domain (termed by its presence in tryptophanyl-, histidyl-, and glutamyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetases). Here, we identify site-selective proteolysis as a mechanism that severs the linkage between the EPRS synthetases in vitro and in vivo Caspase action targeted Asp-929 in the third WHEP domain, thereby separating the two synthetases. Using a neoepitope antibody directed against the newly exposed C terminus, we demonstrate EPRS cleavage at Asp-929 in vitro and in vivo Biochemical and biophysical characterizations of the N-terminally generated EPRS proteoform containing the glutamyl-tRNA synthetase and most of the linker, including two WHEP domains, combined with structural analysis by small-angle neutron scattering, revealed a role for the WHEP domains in modulating conformations of the catalytic core and GSH-S-transferase-C-terminal-like (GST-C) domain. WHEP-driven conformational rearrangement altered GST-C domain interactions and conferred distinct oligomeric states in solution. Collectively, our results reveal long-range conformational changes imposed by the WHEP domains and illustrate how noncatalytic domains can modulate the global structure of tRNA synthetases in complex eukaryotic systems.
Keywords: EPRS; aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase; aminoacylation; biophysics; caspase; glutamyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetase; microscale thermophoresis; neoepitope; neutron scattering; protein conformation; small-angle neutron scattering; transfer RNA (tRNA).
© 2018 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures







Similar articles
-
Evolution of function of a fused metazoan tRNA synthetase.Mol Biol Evol. 2011 Jan;28(1):437-47. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msq246. Epub 2010 Sep 9. Mol Biol Evol. 2011. PMID: 20829344 Free PMC article.
-
Glu-Q-tRNA(Asp) synthetase coded by the yadB gene, a new paralog of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase that glutamylates tRNA(Asp) anticodon.Biochimie. 2005 Sep-Oct;87(9-10):847-61. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2005.03.007. Epub 2005 Apr 8. Biochimie. 2005. PMID: 16164993
-
Origin and evolution of glutamyl-prolyl tRNA synthetase WHEP domains reveal evolutionary relationships within Holozoa.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 26;9(6):e98493. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098493. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24968216 Free PMC article.
-
Substrate selection by aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases.Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1995;(33):40-2. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser. 1995. PMID: 8643392 Review.
-
Glutamyl-tRNA sythetase.Biol Chem. 1997 Nov;378(11):1313-29. Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9426192 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure and Dynamics of the Human Multi-tRNA Synthetase Complex.Subcell Biochem. 2022;99:199-233. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-00793-4_6. Subcell Biochem. 2022. PMID: 36151377
-
Circadian clock regulator Bmal1 gates axon regeneration via Tet3 epigenetics in mouse sensory neurons.Nat Commun. 2023 Aug 24;14(1):5165. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40816-7. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37620297 Free PMC article.
-
Hypomyelinating Leukodystrophy 15 (HLD15)-Associated Mutation of EPRS1 Leads to Its Polymeric Aggregation in Rab7-Positive Vesicle Structures, Inhibiting Oligodendroglial Cell Morphological Differentiation.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Mar 29;13(7):1074. doi: 10.3390/polym13071074. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33805425 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphocode-dependent glutamyl-prolyl-tRNA synthetase 1 signaling in immunity, metabolism, and disease.Exp Mol Med. 2023 Oct;55(10):2116-2126. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-01094-x. Epub 2023 Oct 2. Exp Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37779151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disease-associated mutations in a bifunctional aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase gene elicit the integrated stress response.J Biol Chem. 2021 Oct;297(4):101203. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101203. Epub 2021 Sep 17. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34537243 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Park M. C., Kang T., Jin D., Han J. M., Kim S. B., Park Y. J., Cho K., Park Y. W., Guo M., He W., Yang X. L., Schimmel P., and Kim S. (2012) Secreted human glycyl-tRNA synthetase implicated in defense against ERK-activated tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109, E640–E647 10.1073/pnas.1200194109 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

