Use of statins and the risk of dementia and mild cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 29643479
- PMCID: PMC5895617
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-24248-8
Use of statins and the risk of dementia and mild cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
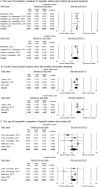
We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to investigate whether the use of statins could be associated with the risk of all-caused dementia, Alzheimer's disease (AD), vascular dementia (VaD), and mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Major electronic databases were searched until December 27th, 2017 for studies investigating use of statins and incident cognitive decline in adults. Random-effects meta-analyses calculating relative risks (RRs) were conducted to synthesize effect sizes of individual studies. Twenty-five studies met eligibility criteria. Use of statins was significantly associated with a reduced risk of all-caused dementia (k = 16 studies, adjusted RR (aRR) = 0.849, 95% CI = 0.787-0.916, p = 0.000), AD (k = 14, aRR = 0.719, 95% CI = 0.576-0.899, p = 0.004), and MCI (k = 6, aRR = 0.737, 95% CI = 0.556-0.976, p = 0.033), but no meaningful effects on incident VaD (k = 3, aRR = 1.012, 95% CI = 0.620-1.652, p = 0.961). Subgroup analysis suggested that hydrophilic statins were associated with reduced risk of all-caused dementia (aRR = 0.877; CI = 0.818-0.940; p = 0.000) and possibly lower AD risk (aRR = 0.619; CI = 0.383-1.000; p = 0.050). Lipophilic statins were associated with reduced risk of AD (aRR = 0.639; CI = 0.449-0.908; p = 0.013) but not all-caused dementia (aRR = 0.738; CI = 0.475-1.146; p = 0.176). In conclusion, our meta-analysis suggests that the use of statins may reduce the risk of all-type dementia, AD, and MCI, but not of incident VaD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4th ed (1994).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

