The basal ganglia and the cerebellum: nodes in an integrated network
- PMID: 29643480
- PMCID: PMC6503669
- DOI: 10.1038/s41583-018-0002-7
The basal ganglia and the cerebellum: nodes in an integrated network
Abstract
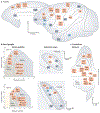
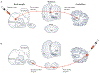
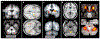
The basal ganglia and the cerebellum are considered to be distinct subcortical systems that perform unique functional operations. The outputs of the basal ganglia and the cerebellum influence many of the same cortical areas but do so by projecting to distinct thalamic nuclei. As a consequence, the two subcortical systems were thought to be independent and to communicate only at the level of the cerebral cortex. Here, we review recent data showing that the basal ganglia and the cerebellum are interconnected at the subcortical level. The subthalamic nucleus in the basal ganglia is the source of a dense disynaptic projection to the cerebellar cortex. Similarly, the dentate nucleus in the cerebellum is the source of a dense disynaptic projection to the striatum. These observations lead to a new functional perspective that the basal ganglia, the cerebellum and the cerebral cortex form an integrated network. This network is topographically organized so that the motor, cognitive and affective territories of each node in the network are interconnected. This perspective explains how synaptic modifications or abnormal activity at one node can have network-wide effects. A future challenge is to define how the unique learning mechanisms at each network node interact to improve performance.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
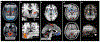
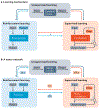
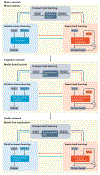
References
-
- Kemp JM & Powell TP The connexions of the striatum and globus pallidus: synthesis and speculation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci. 262, 441–457 (1971). - PubMed
-
- Glickstein M, May JG 3rd & Mercier BE Corticopontine projection in the macaque: the distribution of labelled cortical cells after large injections of horseradish peroxidase in the pontine nuclei. J. Comp. Neurol. 235, 343–359 (1985). - PubMed
-
- Alexander GE, DeLong MR & Strick PL Parallel organization of functionally segregated circuits linking basal ganglia and cortex. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 9, 357–381 (1986). - PubMed
-
- Middleton FA & Strick PL Basal ganglia output and cognition: evidence from anatomical, behavioral, and clinical studies. Brain Cogn. 42, 183–200 (2000). - PubMed
-
- Strick PL, Dum RP & Fiez JA Cerebellum and nonmotor function. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 32, 413–434 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

