The effect of pre-emptive gabapentin on anaesthetic and analgesic requirements in patients undergoing rhinoplasty: A prospective randomised study
- PMID: 29643553
- PMCID: PMC5881321
- DOI: 10.4103/ija.IJA_736_17
The effect of pre-emptive gabapentin on anaesthetic and analgesic requirements in patients undergoing rhinoplasty: A prospective randomised study
Abstract
Background and aims: Hypotensive anaesthesia is necessary in rhinoplasty for better visualisation of surgical field and reduction of surgery time. Gabapentin is a new generation anticonvulsant with anti-hyperalgesic and anti-nociceptive properties. We aimed to investigate the effect of pre-operative administration of oral gabapentin (1200 mg) on anaesthetic requirements and post-operative analgesic consumption and its role in hypotensive anaesthesia for rhinoplasty.
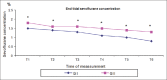
Methods: Seventy adult patients undergoing rhinoplasty, were randomly allocated to two groups. Group I (G I) (n = 35) received gabapentin 1.2 g and Group II (G II) (n = 35) received oral placebo capsules 2 h before surgery. General anaesthesia was maintained with sevoflurane in oxygen-nitrous oxide to maintain bispectral index value between 40 and 60, and remifentanil infusion to keep mean arterial pressure (MAP) at 55-60 mmHg. End-tidal sevoflurane concentration, intra-operative remifentanil consumption and time to intended MAP were recorded. Visual analogue scale (VAS) scores, post-operative analgesic requirements and side effects for the first 24 h were recorded.
Results: G I required significantly lower intra-operative remifentanil (G I = 0.8 ± 0.26 mg and G II = 1.7 ± 0.42 mg; P = 0.001) and end-tidal sevoflurane concentration, with reduced doses of post-operative tramadol and diclofenac sodium. Time to the intended MAP was significantly less in G I than G II (59.1 ± 12.3 vs. 73.6 ± 16.4, respectively, with P = 0.001).
Conclusion: Pre-operative oral gabapentin significantly reduced intra-operative remifentanil and sevoflurane requirements during hypotensive anaesthesia along with decreased post-operative analgesic requirement.
Keywords: Anaesthetic; analgesic; gabapentin; hypotension; rhinoplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mireskandari SM, Karvandian K, Jafarzadeh A, Makarem J, Samadi S, Hajipour A, et al. The effectiveness of intravenous magnesium sulfate for deliberate hypotension in rhinoplasty. Arch Anesth Crit Care. 2015;1:112–5.
-
- Joshi SS, Jagadeesh AM. Efficacy of perioperative pregabalin in acute and chronic post-operative pain after off-pump coronary artery bypass surgery: A randomized, double-blind placebo controlled trial. Ann Card Anaesth. 2013;16:180–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical