Ultrasound guided internal jugular vein cannulation in infants: Comparative evaluation of novel modified short axis out of plane approach with conventional short axis out of plane approach
- PMID: 29643555
- PMCID: PMC5881323
- DOI: 10.4103/ija.IJA_676_17
Ultrasound guided internal jugular vein cannulation in infants: Comparative evaluation of novel modified short axis out of plane approach with conventional short axis out of plane approach
Abstract
Background and aims: Central venous cannulation (CVC) through right internal jugular vein (IJV) route is routinely performed in paediatric patients undergoing major surgery and in those admitted to intensive care units. A novel technique (modified short-axis out-of-plane [MSA-OOP]) to improve first pass success rate of ultrasound-guided IJV CVC in neonates and infants is being compared with conventional SA-OOP method.
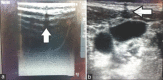
Methods: A total of 120 patients were enroled in the study over a period of 6 months. All paediatric patients with age <1 year and weight <10 kg who underwent a major surgery requiring CVC were included. Patients were randomised to either of the two approaches of ultrasound-guided IJV cannulation; SA-OOP and modified SA-OOP (MSA-OOP). In modified approach, the midline of probe footprint was marked with a radio-opaque barium wire that casted a central acoustic shadow on ultrasound screen.
Results: In MSA-OOP group, 83.1% of patients were cannulated in the first attempt as compared to 49.2% patients in group SA-OOP. Patients in MSA-OOP group required significantly fewer attempts for successful CVC as compared to patients in the SA-OOP group ( MSA-OOP: median = 1, interquartile range [1-1]; SAOOP: median = 2, interquartile range [1-2], P < 0.001, Mann-Whitney U-test).
Conclusion: The use of MSA-OOP ultrasound technique for IJV CVC cannulation results in a higher first-attempt success rate and reduces the number of cannulation attempts.
Keywords: Central venous cannulation; neonates and infants; ultrasound guided vascular access.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mallinson C, Bennett J, Hodgson P, Petros AJ. Position of the internal jugular vein in children. A study of the anatomy using ultrasonography. Paediatr Anaesth. 1999;9:111–4. - PubMed
-
- Nicolson SC, Sweeney MF, Moore RA, Jobes DR. Comparison of internal and external jugular cannulation of the central circulation in the pediatric patient. Crit Care Med. 1985;13:747–9. - PubMed
-
- Quan Z, Tian M, Chi P, Cao Y, Li X, Peng K, et al. Modified short-axis out-of-plane ultrasound versus conventional long-axis in-plane ultrasound to guide radial artery cannulation: A randomized controlled trial. Anesth Analg. 2014;119:163–9. - PubMed
-
- Ullman JI, Stoelting RK. Internal jugular vein location with the ultrasound doppler blood flow detector. Anesth Analg. 1978;57:118. - PubMed
-
- Denys BG, Uretsky BF, Reddy PS. Ultrasound-assisted cannulation of the internal jugular vein. A prospective comparison to the external landmark-guided technique. Circulation. 1993;87:1557–62. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

