Fixation of unstable distal radius fractures by using expandable Intramedullary nailing system in adult patients
- PMID: 29643907
- PMCID: PMC5857012
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.341.14239
Fixation of unstable distal radius fractures by using expandable Intramedullary nailing system in adult patients
Abstract
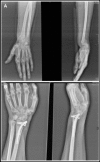
Objective: To present our experience on intramedullary nailing device Sonoma Wrx (Sonoma Orthopedic Products Inc., Santa Rosa, CA, USA) used for internal fixation of extra-articular or simple intra-articular distal radius fractures in adult population.
Methods: This study was conducted from February 2011 to October 2016. A total of 48 patients (mean age 47.3±5.6 years, 35.4% females) with distal radius fracture, who underwent intramedullary distal radius fixation by using Sonoma Wrx were included in this retrospective study. Clinical outcome measures (range of motion [ROM], visual analog scale [VAS]), functional outcomes (Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand [DASH] score and Gartland-Werley score), radiographic scores (Stewart score) and parameters (radial inclination, volar tilt, radial height, radio-ulnar variance) and complications were evaluated.
Results: The total surgery time was 24.3±2.3 minutes. Patients were followed up for 24.7±3.4 weeks. Complete fracture union was obtained at 5.5±0.9 weeks. The postoperative low VAS pain score (1.6±0.93) and high ROM values (76.7° for extension, 78.5° for supination, 80.1° for flexion, and 82.3° for pronation) indicated a very good clinical outcome. DASH score of 8.3±1.5 and Gartland-Werley score of 2.8±4.1 showed good functional outcome. The radiographic Stewart score was 1.0±1.2. Radial inclination, volar tilt, and radial height significantly increased (p<0.001), and radio-ulnar variance decreased (p=0.001) with surgery. No postoperative complication was recorded in 40 patients (83.3%).
Conclusions: Sonoma Wrx, which is an expansible intramedullary elastic locking distal radius nail, offers a good alternative technique for internal fixation of unstable distal radius fractures with the advantage of minimum soft-tissue dissection and related postoperative complications.
Keywords: Distal radius fracture; Internal fixation; Intramedullary nailing.
Figures

References
-
- Porrino JA, Jr, Maloney E, Scherer K, Mulcahy H, Ha AS, Allan C. Fracture of the distal radius: epidemiology and premanagement radiographic characterization. Am J Roentgenol. 2014;203(3):551–559. doi:10.2214/AJR.13.12140. - PubMed
-
- Levin LS, Rozell JC, Pulos N. Distal radius fractures in the elderly. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017;25(3):179–187. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-D-15-00676. - PubMed
-
- Koval K, Haidukewych GJ, Service B, Zirgibel BJ. Controversies in the management of distal radius fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2014;22(9):566–575. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-22-09-566. - PubMed
-
- Xarchas KC, Verettas DA, Kazakos KJ. Classifying fractures of the distal radius: impossible or unnecessary? Review of the literature and proposal of a grouping system. Med Sci Monit. 2009;15(3):67–74. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
