Role of MicroRNAs in Treatment Response in Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 29644941
- PMCID: PMC6463399
- DOI: 10.2174/1568009618666180315160125
Role of MicroRNAs in Treatment Response in Prostate Cancer
Abstract
Prostate cancer (PCa) is the most common non-skin cancer in men worldwide, resulting in significant mortality and morbidity. Depending on the grade and stage of the cancer, patients may be given radiation therapy, hormonal therapy, or chemotherapy. However, more than half of these patients develop resistance to treatment, leading to disease progression and metastases, often with lethal consequences. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short, non-coding RNAs, which regulate numerous physiological as well as pathological processes, including cancer. miRNAs mediate their regulatory effect predominately by binding to the 3'-untranslated region (UTR) of their target mRNAs. In this review, we will describe the mechanisms by which miRNAs mediate resistance to radiation and drug therapy (i.e. hormone therapy and chemotherapy) in PCa, including control of apoptosis, cell growth and proliferation, autophagy, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), invasion and metastasis, and cancer stem cells (CSCs). Furthermore, we will discuss the utility of circulating miRNAs isolated from different body fluids of prostate cancer patients as non-invasive biomarkers of cancer detection, disease progression, and therapy response. Finally, we will shortlist the candidate miRNAs, which may have a role in drug and radioresistance, that could potentially be used as predictive biomarkers of treatment response.
Keywords: MicroRNAs (miRNAs); apoptosis; biomarkers; prostate cancer; radiation and drug therapy; therapy response..
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.org.
Figures
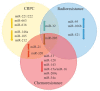
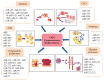

References
-
- Jemal A., Bray F., Center M.M., Ferlay J., Ward E., Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Malik R., Khan A.P., Asangani I.A., Cieslik M., Prensner J.R., Wang X., Iyer M.K., Jiang X., Borkin D., Escara-Wilke J., Stender R., Wu Y.M., Niknafs Y.S., Jing X., Qiao Y., Palanisamy N., Kunju L.P., Krishnamurthy P.M., Yocum A.K., Mellacheruvu D., Nesvizhskii A.I., Cao X., Dhanasekaran S.M., Feng F.Y., Grembecka J., Cierpicki T., Chinnaiyan A.M. Targeting the MLL complex in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Nat. Med. 2015;21:344–352. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Grossfeld G.D., Olumi A.F., Connolly J.A., Chew K., Gibney J., Bhargava V., Waldman F.M., Carroll P.R. Locally recurrent prostate tumors following either radiation therapy or radical prostatectomy have changes in Ki-67 labeling index, p53 and bcl-2 immunoreactivity. J. Urol. 1998;159:1437–1443. - PubMed
-
- He L., Hannon G.J. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004;5:522–531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

