Chiron: translating nanopore raw signal directly into nucleotide sequence using deep learning
- PMID: 29648610
- PMCID: PMC5946831
- DOI: 10.1093/gigascience/giy037
Chiron: translating nanopore raw signal directly into nucleotide sequence using deep learning
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Chiron: translating nanopore raw signal directly into nucleotide sequence using deep learning.Gigascience. 2019 May 1;8(5):giz049. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giz049. Gigascience. 2019. PMID: 31077312 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
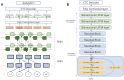
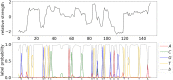
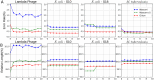
Sequencing by translocating DNA fragments through an array of nanopores is a rapidly maturing technology that offers faster and cheaper sequencing than other approaches. However, accurately deciphering the DNA sequence from the noisy and complex electrical signal is challenging. Here, we report Chiron, the first deep learning model to achieve end-to-end basecalling and directly translate the raw signal to DNA sequence without the error-prone segmentation step. Trained with only a small set of 4,000 reads, we show that our model provides state-of-the-art basecalling accuracy, even on previously unseen species. Chiron achieves basecalling speeds of more than 2,000 bases per second using desktop computer graphics processing units.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Basecalling Using Joint Raw and Event Nanopore Data Sequence-to-Sequence Processing.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Mar 15;22(6):2275. doi: 10.3390/s22062275. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35336445 Free PMC article.
-
Performance of neural network basecalling tools for Oxford Nanopore sequencing.Genome Biol. 2019 Jun 24;20(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1727-y. Genome Biol. 2019. PMID: 31234903 Free PMC article.
-
From squiggle to basepair: computational approaches for improving nanopore sequencing read accuracy.Genome Biol. 2018 Jul 13;19(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s13059-018-1462-9. Genome Biol. 2018. PMID: 30005597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estimated Nucleotide Reconstruction Quality Symbols of Basecalling Tools for Oxford Nanopore Sequencing.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jul 29;23(15):6787. doi: 10.3390/s23156787. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37571570 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond sequencing: machine learning algorithms extract biology hidden in Nanopore signal data.Trends Genet. 2022 Mar;38(3):246-257. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2021.09.001. Epub 2021 Oct 25. Trends Genet. 2022. PMID: 34711425 Review.
Cited by
-
RODAN: a fully convolutional architecture for basecalling nanopore RNA sequencing data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Apr 20;23(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-04686-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 35443610 Free PMC article.
-
MinION rapid sequencing: Review of potential applications in neurosurgery.Surg Neurol Int. 2018 Aug 10;9:157. doi: 10.4103/sni.sni_55_18. eCollection 2018. Surg Neurol Int. 2018. PMID: 30159201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep learning of genomic variation and regulatory network data.Hum Mol Genet. 2018 May 1;27(R1):R63-R71. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddy115. Hum Mol Genet. 2018. PMID: 29648622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sigmoni: classification of nanopore signal with a compressed pangenome index.Bioinformatics. 2024 Jun 28;40(Suppl 1):i287-i296. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae213. Bioinformatics. 2024. PMID: 38940135 Free PMC article.
-
DeepSimulator: a deep simulator for Nanopore sequencing.Bioinformatics. 2018 Sep 1;34(17):2899-2908. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty223. Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 29659695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashton PM, Nair S, Dallman T, et al. .. MinION nanopore sequencing identifies the position and structure of a bacterial antibiotic resistance island. Nature Biotechnology. 2014;33(3):296–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

