Bipartite graphs in systems biology and medicine: a survey of methods and applications
- PMID: 29648623
- PMCID: PMC6333914
- DOI: 10.1093/gigascience/giy014
Bipartite graphs in systems biology and medicine: a survey of methods and applications
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to: Bipartite graphs in systems biology and medicine: a survey of methods and applications.Gigascience. 2020 Jan 1;9(1):giz130. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giz130. Gigascience. 2020. PMID: 31957787 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
The latest advances in high-throughput techniques during the past decade allowed the systems biology field to expand significantly. Today, the focus of biologists has shifted from the study of individual biological components to the study of complex biological systems and their dynamics at a larger scale. Through the discovery of novel bioentity relationships, researchers reveal new information about biological functions and processes. Graphs are widely used to represent bioentities such as proteins, genes, small molecules, ligands, and others such as nodes and their connections as edges within a network. In this review, special focus is given to the usability of bipartite graphs and their impact on the field of network biology and medicine. Furthermore, their topological properties and how these can be applied to certain biological case studies are discussed. Finally, available methodologies and software are presented, and useful insights on how bipartite graphs can shape the path toward the solution of challenging biological problems are provided.
Figures
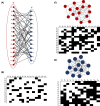
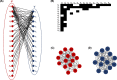
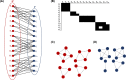
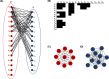


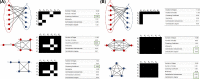


References
-
- Fields S, Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature 1989;340(6230):245–6. - PubMed
-
- Zhu H, Bilgin M, Bangham R et al. . Global analysis of protein activities using proteome chips. Science 2001;293(5537):2101–5. - PubMed
-
- Uetz P, Giot L, Cagney G et al. . A comprehensive analysis of protein-protein interactions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature 2000;403(6770):623–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

