Regulated Proteolysis in Bacteria
- PMID: 29648875
- PMCID: PMC6013389
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-062917-012848
Regulated Proteolysis in Bacteria
Abstract
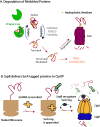
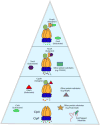
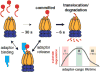
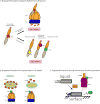
Regulated proteolysis is a vital process that affects all living things. Bacteria use energy-dependent AAA+ proteases to power degradation of misfolded and native regulatory proteins. Given that proteolysis is an irreversible event, specificity and selectivity in degrading substrates are key. Specificity is often augmented through the use of adaptors that modify the inherent specificity of the proteolytic machinery. Regulated protein degradation is intricately linked to quality control, cell-cycle progression, and physiological transitions. In this review, we highlight recent work that has shed light on our understanding of regulated proteolysis in bacteria. We discuss the role AAA+ proteases play during balanced growth as well as how these proteases are deployed during changes in growth. We present examples of how protease selectivity can be controlled in increasingly complex ways. Finally, we describe how coupling a core recognition determinant to one or more modifying agents is a general theme for regulated protein degradation.
Keywords: AAA+ proteases; ClpP; ClpX; Lon.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

